Overview of Dark Websites
Dark websites refer to hidden parts of the internet that are not indexed by standard search engines and require specific tools or configurations to access. These sites often operate on encrypted networks, such as the Tor network, providing a level of anonymity for both visitors and operators. While some dark websites are used for legitimate purposes like protecting privacy and free expression, others may facilitate illegal activities. Understanding the nature and structure of dark websites is essential for cybersecurity professionals and users alike to navigate the digital landscape safely.
Definition and Characteristics of Dark Websites
Dark websites refer to online platforms that are intentionally hidden from standard search engines and accessible only through specific networks or tools, such as the Tor network. These websites operate outside the traditional public internet, providing a level of anonymity and privacy for their users and operators. They are often associated with activities that require discretion, ranging from legitimate privacy-focused communications to illicit enterprises.
Characteristics of dark websites include their use of encrypted and hidden infrastructure, making them difficult to find or access without specialized software. They typically have URLs ending with the “.onion” domain extension, which is specific to the Tor network. Content hosted on dark websites is often designed to remain anonymous, with providers employing measures to conceal their identities and locations. This inherent privacy makes dark websites a unique segment of the internet environment, distinguished by their secretive and often encrypted nature.
Differences Between Dark Websites and the Dark Web
Dark websites are a segment of the internet that functions outside the reach of traditional search engines and standard browsing methods. These websites are intentionally hidden and often require special access credentials or specific software to view. They are used for various purposes, ranging from private communications to legitimate anonymity needs, but can also be associated with illicit activities.
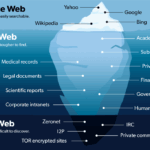
The key difference between dark websites and the dark web lies in their scope and definition. The dark web encompasses all websites that are not indexed by standard search engines and require specialized software, such as Tor or I2P, to access. Within this broader category, dark websites are specific sites operating on the dark web that are intentionally hidden from public view. In essence, the dark web is a collection of hidden networks, whereas dark websites are individual sites hosted within these networks.
Understanding the distinctions is important for recognizing the various uses and risks associated with dark websites. While some serve legitimate purposes like confidential communication or privacy protection, others are involved in illegal activities, including black markets and illicit exchanges. Users should exercise caution and be aware of the privacy and security implications when navigating or discussing dark websites and the dark web as a whole.
Security and Anonymity Features of Dark Websites
Dark websites are parts of the internet that are not accessible through standard search engines and require specific software or configurations to access. They are often associated with clandestine activities but also serve legitimate purposes such as privacy protection and anonymous communication. These websites operate on overlay networks like the Tor network, which anonymizes user identities and server locations, making tracing difficult. By leveraging advanced security and anonymity features, dark websites provide a platform where users can communicate, share information, and conduct transactions without revealing their true identities or physical locations.
Security features of dark websites include encrypted communications that safeguard data against interception and tampering. The use of layered encryption through networks like Tor ensures that both the user’s identity and the website’s hosting details remain confidential. Additionally, many dark websites implement strong authentication mechanisms and employ security protocols to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate risks associated with malicious attacks. These measures are crucial for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive activities conducted on these sites.
Furthermore, anonymity features are central to the operation of dark websites. Users typically access these sites via specialized browsers that mask IP addresses and encrypt traffic, providing a high level of privacy. This environment allows for free expression and the exchange of information without fear of censorship or persecution. While dark websites can facilitate illegal activities, their security and anonymity features are instrumental in supporting whistleblowers, journalists, activists, and others seeking to operate securely in oppressive regimes or risky environments.
Structure and Content of Dark Websites
Dark websites are hidden parts of the internet that operate outside the boundaries of conventional search engines and accessible networks. Their structure typically involves encrypted and anonymized connections, making them difficult to locate and monitor. The content within these sites varies widely, often including forums, marketplaces, and information resources that require specific access methods. Understanding the layout and organization of dark websites is crucial for users who seek to explore these hidden digital landscapes safely and responsibly. Some dark websites are designed with layered security measures, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive or confidential information. To explore examples of such sites, including those hosting unique content, you may visit sources like dark websites. Knowing about the structure and content organization of these sites can help navigate this clandestine online realm more effectively.
Design Elements and User Interface
Dark websites are a unique segment of the internet that often operate outside the traditional accessible web. These sites are characterized by their distinctive structure and content, designed to provide anonymity and privacy for users and operators alike. The architecture of dark websites typically relies on hidden directories and encrypted connections, making their exact layout less visible to casual browsers. The content commonly includes secure forums, clandestine marketplaces, or private communications, formatted to prioritize security and confidentiality.
When it comes to design elements, dark websites often employ a palette dominated by dark hues such as black, deep grays, and muted tones. This not only helps maintain user anonymity but also reduces eye strain during extended browsing sessions. Visual elements are generally minimalist, focusing on text clarity and essential icons rather than elaborate graphics. User interfaces are streamlined to facilitate quick navigation and ensure ease of access to crucial features while minimizing distractions. Navigation menus are typically simple and straightforward, often through text links or basic buttons, allowing users to move seamlessly through the site’s sections.
The user interface on dark websites emphasizes functionality and security. Clear, concise labeling and intuitive layout help users find what they need rapidly. Since these sites often serve sensitive purposes, login forms and access points are designed with high security in mind, often incorporating encryption protocols and anonymizing tools. While aesthetics may be minimalistic, the overall design aims to foster trust and ease of use, encouraging users to engage with the content confidently. Understanding the structure and content of dark websites highlights their focus on privacy and secure communication, making them distinct from regular websites with more open and visually vibrant designs.
Common Use Cases and Purposes
Dark websites refer to online platforms that are intentionally hidden from traditional search engines and accessible only through specific networks or technologies. These sites often lack visibility on standard browsers and are typically hosted on encrypted networks, making them difficult for casual users to discover. The structure of these websites tends to prioritize anonymity and security, often employing decentralized hosting methods, encrypted connections, and minimal design to maintain privacy. Their content varies widely, but it generally includes forums, marketplaces, or resources that require restricted access or anonymity.
In terms of content, dark websites are frequently used for purposes that necessitate privacy and security, such as confidential communications, private marketplaces, or forums for sensitive topics. This environment allows users to maintain anonymity while exchanging information, sharing files, or conducting activities without fear of surveillance or censorship. The layout is typically simple, prioritizing functionality over aesthetics, with security measures embedded to protect users’ identities and data.
Common use cases and purposes of dark websites encompass various activities. They are often used for secure communication and whistleblowing, providing a safe space for individuals to share information without risking repercussions. Dark websites also host black markets for illicit goods and services, such as stolen data or counterfeit products. Additionally, certain communities utilize dark websites for political activism, particularly in regions where free expression is suppressed. The discreet nature of dark websites enables these diverse activities to proceed while maintaining user anonymity and protecting against external threats.
Access Restrictions and Authentication Mechanisms
Dark websites are online spaces that operate outside the reach of standard search engines and are often associated with private or anonymous activities. Their structure typically consists of hidden pages accessible only through specific means, making them distinct from conventional websites. These sites frequently employ layered navigation systems and hidden directories, which require specialized knowledge to access or locate. The content on dark websites can vary widely, ranging from legitimate privacy-focused platforms to illicit marketplaces or forums.
One key characteristic of dark websites is the use of access restrictions and authentication mechanisms to control user entry. These restrictions may include password protection, invitation-only access, or the use of anonymous network protocols. Authentication mechanisms such as cryptographic keys, two-factor authentication, or specialized login systems help ensure only authorized users can access sensitive or discrete content. The implementation of these security measures often aims to preserve user anonymity and prevent unauthorized surveillance.
In terms of structure, dark websites often prioritize security and privacy over ease of access. They may utilize layered encryption, decentralized hosting, or network anonymization tools like the Tor network to obfuscate their locations and identities. The content is typically stored in hidden directories or behind multiple layers of authentication, making crawling and indexing by standard search engines extremely difficult. This structural design contributes to the secretive and private nature of dark websites, where the focus is on confidentiality and controlled access.
Overall, the architecture and content management of dark websites reflect their purpose of maintaining anonymity and restricting access. Understanding these aspects is crucial for cybersecurity professionals, researchers, and law enforcement agencies working to monitor and analyze these hidden corners of the internet. While they serve legitimate privacy needs for some users, they can also host illicit activities, highlighting the importance of robust access restrictions and authentication mechanisms in ensuring security and privacy on these platforms.
Accessing Dark Websites
Exploring dark websites involves navigating hidden parts of the internet that are not accessible through traditional search engines or standard browsers. These sites operate on specialized networks, providing a layer of anonymity for users and website operators. Accessing dark websites requires understanding how these networks function and using the appropriate tools, such as the Tor browser, to safely explore content that is often hidden from the public eye. It’s essential to approach this realm with caution, as it can host both legitimate activities and illegal operations. For those interested in learning more about secure access, exploring reputable resources on dark web navigation can provide valuable insights.

Required Browsers and Software
Accessing dark websites typically requires specialized software and browsers that support anonymity and encryption. These websites are part of the deep web, which is not indexed by standard search engines and often hosts both legitimate and illicit activities. To explore dark websites safely, users must utilize tools designed to anonymize their online presence and protect their privacy.
- In this web design showcase, you’ll find 60 hand-picked websites that use a primarily dark color palette.
- It’s a little like using “Smart Invert” on an iPhone—light colors will turn bright, but it’ll leave images alone.
- The consistent use of shades of orange and red creates a cohesive, distinctive design that highlights the agency’s data solutions.
- These sites cover a range of niches, from agencies to personal portfolios, business websites, and more.
The most commonly used browser for accessing dark websites is the Tor Browser. Tor, which stands for The Onion Router, routes internet traffic through a worldwide volunteer overlay network composed of thousands of relays, concealing users’ locations and usage from surveillance and traffic analysis. This browser is specifically configured to access .onion sites, which are characteristic of dark websites and provide an additional layer of security.
In addition to the Tor Browser, other security-focused tools may be employed, such as virtual private networks (VPNs) to add further anonymity or specialized operating systems like Tails that are designed for privacy and security. It is crucial to ensure that all software used is up-to-date, as outdated versions can contain vulnerabilities that threaten user safety. When browsing dark websites, avoiding personal information disclosure and refraining from downloading files are important precautions to prevent potential security risks.
Due to the nature of dark websites and the potential for exposure to illegal or harmful content, users should proceed with caution and be aware of legal implications and safety concerns. Proper preparation, including using trusted browsers, encrypted connections, and security protocols, is essential for those wishing to access these parts of the internet responsibly and securely.

Using Tor and Other Anonymity Networks
Accessing dark websites involves navigating parts of the internet that are not indexed by traditional search engines and require specific tools to ensure privacy and anonymity. These sites are often associated with privacy-focused activities or illicit content, making it essential for users to understand the appropriate methods and precautions involved. To access such sites, individuals typically rely on anonymity networks like Tor, which anonymize internet traffic by routing it through a series of volunteer-operated servers, making it difficult to trace the user’s identity or location.
Using Tor is the most common way to explore dark websites securely. Tor, short for The Onion Router, encrypts and bounces your internet traffic across multiple nodes worldwide, providing a layer of privacy that is difficult to breach. When using Tor, users connect to a specialized browser designed for this network, which automatically directs browsing activity through the Tor network. This level of anonymity is crucial for accessing dark websites where privacy concerns are paramount. However, it’s important to remember that while Tor provides significant privacy benefits, it does not guarantee complete security, and users should remain cautious about the risks involved.
Besides Tor, other anonymity networks like I2P and Freenet also facilitate access to content within the dark web. Each network employs different technologies to ensure user privacy and secure communication. For instance, I2P creates a private network of encrypted tunnels to protect user identities, making it suitable for private messaging and publishing. Similarly, Freenet allows users to share and publish information anonymously. When exploring dark websites, it’s essential to understand the differences between these networks and choose the one that best fits your needs.
Practicing good security hygiene, such as avoiding revealing personal information, using encrypted communication tools, and keeping software up to date, is vital when accessing these hidden parts of the internet. Remember that while dark websites may serve legitimate purposes like journalistic integrity and privacy advocacy, they can also host illegal activities. Users should exercise caution, adhere to local laws, and prioritize safety when engaging with these platforms. Proper understanding and responsible behavior are key to navigating dark websites securely and ethically.
Navigational Challenges and Precautions
Accessing dark websites involves navigating parts of the internet that are not indexed by traditional search engines and require specific tools or configurations to access. These sites often operate on the Tor network or other anonymizing networks, providing users with enhanced privacy and anonymity. However, venturing into these areas presents significant challenges due to their complex navigation structures and the need for specialized browser setups.
Navigational challenges in dark websites stem from their deliberately obscure and unorganized layouts. Unlike surface web sites, which are designed for user-friendliness and easy access, dark websites often lack straightforward navigation menus, relying instead on hidden links or directories. This can make it difficult for users to find desired content quickly, increasing the chance of accidental encounters with malicious or illegal material.
Users must exercise caution and adopt proper precautions when accessing these sites to protect their privacy and security. Using reputable anonymizing tools, such as the Tor Browser, is essential for maintaining anonymity. It is also advised to avoid downloading files or clicking on suspicious links, as these actions can compromise device security or lead to legal issues. Staying informed about potential risks and adhering to safe browsing practices can help mitigate dangers associated with dark websites.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Navigating the complexities of dark websites requires a thorough understanding of the legal and ethical considerations involved. These concealed parts of the internet often host a range of activities, some lawful and others potentially illegal, raising important questions about morality, security, and legality. Ensuring responsible engagement and awareness of the implications is crucial for anyone exploring this clandestine online world to maintain ethical standards and adhere to applicable laws.
Legitimate Uses of Dark Websites
Dark websites, often associated with anonymous and untraceable online activity, present complex legal and ethical considerations that must be carefully navigated. While some of these sites are used for illicit purposes, others serve legitimate roles, such as protecting privacy rights, supporting free expression, and enabling secure communication for whistleblowers or journalists in repressive environments.
Engaging with dark websites raises important legal questions related to jurisdiction, law enforcement, and the enforcement of regulations. Activities conducted on these sites may violate laws surrounding illegal marketplaces, illicit content, or cybercrime, and individuals should be aware of the potential consequences. It is essential to distinguish between legitimate uses—like safeguarding privacy and facilitating activism—and unlawful activities that can harm individuals and society.
From an ethical standpoint, respecting user privacy and freedom of speech is paramount. Dark websites can serve as vital tools for vulnerable populations and organizations operating under oppressive regimes. However, they can also be exploited for malicious purposes, such as trafficking, terrorism, or distributing illegal content. Therefore, clear boundaries and responsible usage guidelines are crucial to ensure these platforms serve constructive and lawful roles.
Legitimate uses of dark websites include providing anonymity for journalists, activists, and victims of persecution, as well as enabling confidential communication for whistleblowers. They support free expression in environments where the open internet is heavily censored or monitored. For these reasons, understanding the distinction between acceptable and harmful activities on dark websites is essential for navigating their legal and ethical landscape responsibly.
Illegal Activities and Risks

Exploring the realm of dark websites involves understanding the complex legal and ethical considerations that come with such environments. These sites often operate outside the boundaries of conventional regulation, raising significant concerns about legality, morality, and safety. Engaging with dark websites can expose individuals to a variety of illegal activities, including illicit trade, cybercrime, and the distribution of illegal content. Such involvement can lead to severe legal repercussions, including criminal charges, fines, and imprisonment. Moreover, the clandestine nature of dark websites complicates enforcement efforts, making it difficult to identify and prosecute offenders.
There are also substantial ethical issues associated with accessing or supporting dark websites. These platforms can foster environments where harm, exploitation, or illegal transactions occur unchecked. Using or even unintentionally contributing to these sites may be viewed as condoning or enabling unlawful behavior. Users should be aware of the potential risks, such as exposure to malicious software, scams, or harmful content, which can have personal and financial consequences. In particular, engaging with sites like dark websites presents a heightened risk of encountering illegal activities that could jeopardize one’s digital security and legal standing.
Overall, individuals must be cautious and thoroughly understand the legal and ethical implications involved in navigating dark websites. Despite the allure of anonymity, the significant risks involved—ranging from legal penalties to exposure to criminal activities—highlight the importance of adhering to lawful and morally responsible online behaviors. Staying informed and vigilant helps protect personal integrity and ensures compliance with applicable laws and ethical standards in the digital space.
Impact on Privacy and Data Security
Dark websites, also known as the dark web, operate on encrypted networks that are intentionally hidden from search engines and the general internet. While they can serve legitimate purposes such as protecting privacy for whistleblowers, journalists, and activists, they also pose significant legal and ethical challenges. Navigating the dark web requires careful consideration of the legal frameworks governing online activities in various jurisdictions and adherence to ethical standards to prevent involvement in illicit activities.
One of the primary concerns associated with dark websites is their potential use for illegal activities, including the sale of illicit drugs, weapons, stolen data, and other unlawful goods. Engaging in or facilitating such activities can have serious legal consequences, regardless of whether the platform is publicly accessible or part of the dark web. Ethical considerations also extend to respecting the rights of individuals and avoiding participation in malicious or harmful transactions.
Impact on privacy and data security is a particularly salient issue when exploring dark websites. While they often emphasize privacy and anonymity, these same features can be exploited by malicious actors to commit crimes without fear of detection. Ensuring law enforcement can investigate criminal activities, while simultaneously safeguarding innocent users’ privacy, requires a delicate balance. Users must be aware of the risks involved and ensure they take appropriate measures to protect their personal information and secure their devices from malware and other security threats commonly associated with dark website activities.
Overall, engaging with dark websites demands a thorough understanding of the legal and ethical landscape, alongside a commitment to maintaining high standards of data security and privacy. Responsible navigation is crucial to mitigate legal risks, uphold ethical principles, and protect individual privacy in these hidden corners of the internet.
Dark Websites and Cybersecurity
Dark websites are hidden parts of the internet that are not accessible through standard search engines or browsers. Often associated with illegal activities, these sites operate on anonymizing networks that safeguard the privacy of their users. The anonymity provided by dark websites makes them a focal point for cybersecurity concerns, as malicious actors and cybercriminals frequently utilize these platforms to conduct illicit transactions, distribute malware, or plan cyberattacks. Understanding the vulnerabilities and risks associated with dark websites is crucial for organizations aiming to bolster their cybersecurity defenses and monitor potential threats in this hidden digital landscape. For those interested in exploring secure access to the dark web, some URL addresses are available through specialized underground networks. Such sites can be utilized responsibly to investigate cybersecurity threats and enhance protective measures against cybercrime.
Common Threats Associated with Dark Websites
Dark websites are hidden parts of the internet that are not accessible through standard search engines or browsers. They operate on encrypted networks, often using privacy-focused tools like Tor, to provide anonymity and secure communication for users. While these sites serve legitimate purposes such as protecting privacy, they are also frequently associated with illicit activities. The covert nature of dark websites makes them a significant concern for cybersecurity professionals and law enforcement agencies alike.
One of the main cybersecurity challenges posed by dark websites is the facilitation of illegal transactions and activities. These sites often host marketplaces for drugs, weapons, stolen data, and counterfeit documents. The anonymity provided by the dark web enables cybercriminals to operate with minimal risk of detection, making it difficult to track down perpetrators and shut down illegal operations.
Common threats associated with dark websites include the distribution of malware and ransomware. Cybercriminals frequently use these platforms to distribute malicious software to unsuspecting users or to coordinate ransomware attacks against organizations. The dark web also serves as a hub for trading stolen personal and financial information, which can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and other cybercrimes if exploited.
Another concern is the proliferation of cybercriminal forums and marketplaces where hackers share hacking tools, techniques, and credentials. These forums facilitate the planning and execution of cyber-attacks, increasing the risks faced by individuals and organizations. Additionally, dark websites are often used for coordinating cyber espionage efforts, targeting government agencies, businesses, and individuals for espionage or sabotage.
To combat these threats, cybersecurity measures include monitoring dark websites for illegal activity, employing advanced threat detection systems, and educating users about safe browsing practices. Organizations are encouraged to implement comprehensive security protocols and stay vigilant against potential cyber threats originating from the dark web.
Understanding the nature of dark websites and the associated cybersecurity risks is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect sensitive information and maintain digital security. While these sites serve some legitimate privacy needs, their potential for misuse underscores the importance of ongoing vigilance in cybersecurity efforts.
Protection Measures for Users
Dark websites are hidden parts of the internet that are not accessible through standard search engines and require specific software or configurations to access. Often associated with illegal activities, these sites operate on encrypted networks, providing a level of anonymity for both users and administrators. While some dark websites host legitimate content or serve as platforms for free expression, many are exploited for cybercriminal purposes, making cybersecurity a critical concern for users who access or encounter these sites.
Given the clandestine nature of dark websites, cybersecurity measures are essential to protect users from potential threats such as malware, scams, identity theft, and data breaches. Here are key protection strategies:

- Use strong, unique passwords to prevent unauthorized access to viewing or interacting with dark websites.
- Employ advanced security tools like virtual private networks (VPNs) and security-focused browsers to maintain anonymity and mitigate tracking risks.
- Keep software and antivirus programs up to date to defend against malicious code and vulnerabilities often encountered on dark websites.
- Be cautious of phishing attempts and suspicious links that may be designed to harvest personal information or install malware.
- Limit sharing personal information to reduce exposure in case of malicious intent.
- Stay informed about cybersecurity threats related to dark web activities to better recognize potential dangers.
- Use secure communication channels when necessary, avoiding unverified or unsecured messaging platforms.
Understanding the risks associated with dark websites and implementing these protection measures can significantly reduce the threat of cyberattacks. Users should remain vigilant and exercise caution when navigating or interacting with content on these concealed parts of the internet, prioritizing cybersecurity to stay safe in digital environments.
Monitoring and Law Enforcement Efforts
Dark websites, often associated with the hidden corners of the internet, play a complex role in cybersecurity, law enforcement, and digital privacy. These sites operate on encrypted networks and are not accessible through standard browsers, making them both a haven for illicit activities and a challenge for authorities seeking to combat cybercrime. The anonymity provided by dark websites allows users to buy and sell stolen data, counterfeit goods, and other illegal services without revealing their identities. This environment necessitates sophisticated monitoring tools and strategic law enforcement initiatives to combat cyber threats while respecting privacy rights.
Monitoring dark websites requires advanced cybersecurity techniques and persistent surveillance efforts. Agencies employ specialized software that detects suspicious activity, tracks digital footprints, and intercepts illegal transactions. Collaborations between national security entities, private cybersecurity firms, and international organizations are vital to effectively monitor and respond to threats emerging from these hidden online spaces. However, the covert nature of dark websites complicates efforts, demanding continuous innovation in investigative approaches.
Law enforcement efforts aim to dismantle illegal operations without infringing on lawful privacy. This involves coordinated investigations, undercover operations, and global intelligence sharing to identify and apprehend cybercriminals. While disrupting activities on dark websites is crucial, it also raises important questions about digital rights and the balance between security and privacy. Overall, combating the threats posed by dark websites is an ongoing challenge that requires a multi-faceted approach combining technology, collaboration, and legal measures.
Future of Dark Websites
The future of dark websites is a fascinating and complex topic that continues to evolve alongside advances in technology and cybersecurity. As the digital landscape expands, dark websites are likely to play an increasingly significant role, serving various purposes from privacy protection to illicit activities. Exploring this realm offers insights into how these hidden corners of the internet might adapt and transform in response to both technological innovations and regulatory pressures. With ongoing developments, understanding the trajectory of dark websites is essential for cybersecurity professionals, researchers, and users alike.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
The future of dark websites is poised to evolve significantly as emerging trends and technologies continue to shape digital anonymity and privacy. As online users become increasingly concerned about data security and surveillance, more individuals and organizations are exploring hidden web spaces to conduct confidential activities. These platforms often operate outside traditional web search indexes, offering a space for privacy-focused interactions and information sharing. Advancements in encryption, decentralized web infrastructure, and anonymizing tools are expected to play a pivotal role in the development of these sites. Dark websites are likely to become more sophisticated, leveraging innovative technologies to enhance security and user anonymity. However, this growth also raises important questions about regulation, security risks, and ethical considerations that will need to be addressed as the dark web continues to expand. Overall, the trajectory suggests a future where dark websites are integral to supporting privacy-centric online ecosystems while balancing societal and legal implications.
Challenges in Regulation and Control
The future of dark websites presents a complex landscape shaped by technological advancements, evolving legal frameworks, and shifting societal attitudes. These clandestine platforms, often accessed through anonymizing networks, serve a variety of purposes ranging from privacy protection to illicit activities. As digital privacy concerns grow, the demand for secure and anonymous browsing options may lead to increased usage of dark websites. However, this evolution also raises significant challenges for regulation and oversight, as authorities struggle to monitor and control activities occurring on these hidden parts of the internet.
One of the primary challenges in regulating dark websites is their inherently decentralized and encrypted nature. This makes traditional methods of surveillance and enforcement less effective, complicating efforts to combat illegal activities such as drug trafficking, human trafficking, and cybercrime. Governments and law enforcement agencies are exploring new technological solutions, but balancing security with privacy rights remains a contentious issue. Additionally, the international nature of dark websites complicates jurisdictional enforcement, as activities often span multiple countries with differing legal standards.
The future of dark websites will likely involve ongoing technological innovation. As tools for anonymity and encryption improve, these platforms may become even more resilient against regulation. Conversely, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning could assist authorities in identifying patterns and detecting illegal activity more efficiently. Public perception and societal attitudes toward privacy and online freedom will play a significant role in shaping legal and regulatory responses. Ensuring a balance between protecting individual rights and preventing misuse of dark websites will be critical in navigating this complex digital frontier.
Potential Developments in Accessibility and Security
The future of dark websites presents a complex landscape shaped by technological advancements, emerging security challenges, and evolving accessibility needs. As digital privacy becomes increasingly prioritized, these clandestine online spaces are expected to undergo significant transformations that influence how users access and interact with content. Innovations in encryption and anonymity tools may further enhance privacy for users, but they also necessitate stricter security measures to prevent malicious activities. Additionally, developments aimed at improving accessibility could make dark websites more usable for individuals with disabilities, ensuring a broader range of users can navigate these platforms safely and efficiently. The balance between maintaining the anonymity that defines dark websites and ensuring security and accessibility will be a key focus for developers and security experts moving forward. As this ecosystem evolves, it is crucial to develop responsible frameworks that protect user privacy while mitigating risks associated with illegal activities often linked to such sites.