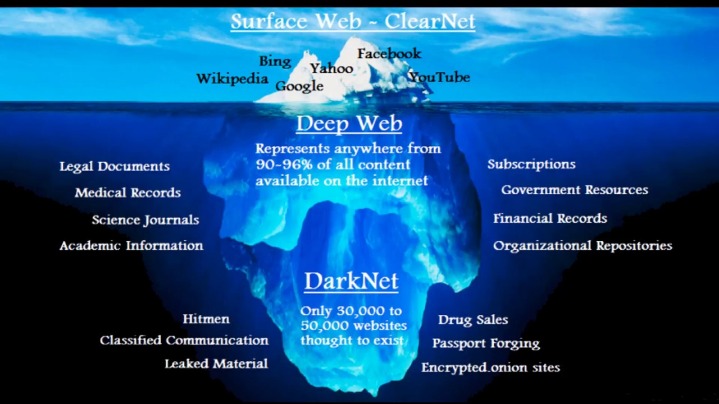
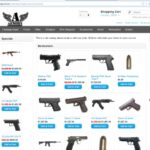
Overview of Dark Web Marketplaces (DWMs)
The dark web market scene comprises an array of clandestine platforms where a wide range of goods and services are bought and sold beyond the reach of traditional internet. These marketplaces, often accessed via specialized networks, facilitate transactions involving illicit items, stolen data, and other restricted products. Understanding the landscape of these platforms is crucial for security professionals, researchers, and law enforcement agencies. A comprehensive dark web market list offers insight into the prominent and emerging marketplaces operating within this shadowy digital environment. Exploring these platforms, such as the marketplace accessible through the links provided, can shed light on current trends and the scope of illegal activities on the dark web. The dark web market list continuously evolves, reflecting shifts in technology, law enforcement efforts, and user demand, making it essential to stay informed about the key players in this covert online economy.
History and Evolution of DWMs
Dark Web Marketplaces (DWMs) are digital platforms hosted on the dark web that facilitate the buying and selling of a wide range of illegal goods and services. These marketplaces operate anonymously, leveraging encrypted networks to shield the identities of both vendors and customers. As a significant part of the dark web ecosystem, DWMs have gained notoriety for their role in facilitating illicit transactions related to drugs, weapons, stolen data, and other prohibited items. A comprehensive dark web market list offers insight into the various platforms that have emerged over time, demonstrating the evolving nature of these clandestine markets.
The history and evolution of DWMs trace back to the early days of the dark web, with one of the first notable marketplaces being Silk Road, launched in 2011. Silk Road pioneered the use of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, allowing for relatively anonymous transactions. Its success and popularity prompted the creation of numerous other marketplaces, each attempting to improve on features such as security, user interface, and escrow services to build trust among users. Over time, these markets faced relentless law enforcement actions, leading to shutdowns and the emergence of new versions with improved security measures, decentralized hosting, and more sophisticated features.
Throughout their evolution, dark web market lists have expanded significantly, showcasing a wide variety of platforms catering to different niches and regions. The rise of decentralized marketplaces and multi-marketplace networks reflects ongoing adaptability in response to crackdowns and technological advancements. Modern DWMs tend to prioritize user safety, privacy, and operational resilience, often implementing multi-factor authentication, decentralized hosting, and encrypted communication channels. Despite ongoing efforts to eradicate or regulate them, these marketplaces continue to evolve, driven by demand and technological innovation, making the dark web market list a dynamic and critical resource for understanding the scope and trajectory of these clandestine networks.
Main Characteristics and Technologies
The dark web market list is a comprehensive catalog of clandestine online platforms operating within the dark web, primarily facilitating anonymous transactions for a wide range of goods and services. These marketplaces have gained notoriety for enabling transactions outside traditional regulatory frameworks, often involving illegal items such as drugs, weapons, and stolen data. Understanding the main characteristics and underlying technologies of these Dark Web Marketplaces (DWMs) is essential for grasping their operational dynamics and underlying risks.
Dark web marketplaces are typically distinguished by several core features. They often rely on anonymity-focused tools and protocols to ensure user privacy and secure transactions. These platforms usually operate on encrypted networks that shield identities and locations of participants, making law enforcement investigations challenging. Many DWMs are structured similarly to conventional e-commerce sites, with product listings, vendor reviews, and payment systems, but are hosted on hidden services accessible only through special browsers.
The technologies underpinning these marketplaces mainly include:
- Tor Network: The primary infrastructure enabling access to hidden services, providing a layered encryption system that anonymizes user traffic and website hosting.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies such as Bitcoin and Monero are predominantly used for transactions, offering decentralized and pseudonymous payment methods that further protect user identities.
- Deep Web Hosting: Many DWMs are hosted on encrypted servers that are not indexed by standard search engines and are only accessible via specific software or URLs.
- Security Protocols: Advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and sometimes decentralized hosting are employed to secure platforms against takedown efforts and hacking.
The dark web market list serves as a vital resource for navigating these hidden platforms, providing updated information on active marketplaces, their features, and operational nuances. Due to the ever-changing landscape of DWMs, the list must be frequently updated to reflect closures, new entries, or altered functionalities.
In summary, dark web marketplaces operate within a complex ecosystem of advanced technologies and anonymity techniques. The dark web market list offers an organized overview of these platforms, enabling users to understand their main characteristics and the technological infrastructure that sustains their operation. Recognizing these factors is crucial for comprehending the broader implications of dark web activities and the ongoing efforts to monitor and regulate them.
Popular Platforms and Their Specializations
The dark web market list offers insight into the clandestine marketplaces operating on the dark web, which serve as hubs for a variety of illicit transactions. These platforms are not accessible through traditional search engines and require specialized software such as Tor to access. Understanding the landscape of dark web marketplaces is essential for recognizing the scope and diversity of activities they facilitate.
Dark Web Marketplaces (DWMs) vary widely in their focus and functionalities. Some platforms specialize in the sale of illegal drugs, firearms, or counterfeit items, while others focus on hacking tools, stolen data, or illegal services. The dark web market list often highlights prominent platforms known for hosting large-scale or niche markets, providing an overview of the ecosystem and its evolution over time.
Among the most popular platforms, certain sites have gained notoriety due to their size, security features, and the variety of listings they host. These platforms usually operate with a high degree of anonymity and employ escrow systems to facilitate transactions securely. Many DWMs also have their own rules, community standards, and reputation systems to maintain a level of trust among users.
Each marketplace tends to have its own specialization, attracting different user bases and vendors. For example, some markets focus primarily on the sale of pharmaceuticals and chemicals, while others may emphasize digital goods like hacking tools or stolen credentials. The dark web market list serves as a valuable resource, cataloging these platforms to help users and researchers understand their characteristics, operational methods, and the risks involved in interactions with them.
Key Features of Dark Web Market List
The dark web market list serves as a crucial resource for navigating the anonymous marketplaces operating within the hidden layers of the internet. These markets often facilitate a wide range of transactions, from legal to illicit activities, making it essential for users to understand their key features. The dark web market list provides detailed information on various platforms, including their security measures, user interfaces, and types of goods and services offered. This knowledge helps users choose reputable sites and avoid scams or illegal content. For example, some markets prioritize privacy and encryption to protect user identities, while others may prioritize a broad selection of items. Exploring the dark web market list can also reveal the evolving landscape of these marketplaces and their unique functionalities, such as escrow services and feedback systems. One notable example can be found at a secure marketplace, accessible through specific entry points, which demonstrates the importance of trustworthy and well-maintained platforms in this environment. Understanding these features is essential for anyone looking to access or study dark web markets responsibly and securely.
Listing Attributes and Data Collection Methods
The dark web market list serves as a comprehensive directory of online marketplaces operating within the dark web environment. These listings provide users with essential information about various platforms, including their functionalities, security features, and areas of specialization. A well-structured dark web market list helps users navigate the complex landscape of hidden online marketplaces, ensuring they can find the services or products they seek while maintaining safety and anonymity.
Key attributes of dark web market listings include details such as marketplace names, descriptions, categories, vendor ratings, and user reviews. These attributes assist users in assessing the reliability and reputation of different markets, thereby reducing potential risks. Additionally, listings often include information on available payment methods, security protocols, and operational statuses, which are crucial for users to make informed decisions.
Data collection methods for maintaining an accurate and up-to-date dark web market list involve various techniques. Automated scraping tools are frequently used to gather information from multiple dark web sources, though they must operate carefully to avoid detection. Manual research by cybersecurity experts also plays a vital role in verifying the legitimacy of marketplaces and tracking changes in their operations. Combining these methods ensures that the dark web market list remains current and reliable, providing a valuable resource for those navigating the dark web.
Categories of Products and Services
The dark web market list serves as a comprehensive directory that catalogues various online marketplaces operating within the dark web. These markets are designed to facilitate anonymous transactions and provide a wide array of products and services that are often not available through conventional channels. A key feature of the dark web market list is its detailed categorization, allowing users to easily navigate and find specific items or services they are interested in. This organization enhances user experience and streamlines the process of locating desired listings.
Among the notable features of the dark web market list are the security measures implemented by these platforms, which include encryption, VPN requirements, and marketplace reputations. These features are essential to preserve user anonymity and protect transactions from malicious activities. The marketplace list also typically highlights recent updates, the status of each site, and user reviews, contributing to transparency and trustworthiness in this clandestine ecosystem. Such features make the dark web market list an invaluable resource for understanding the scope and scale of illegal and unregulated activities carried out on the dark web.
In terms of categories, the dark web market list encompasses a wide range of products and services. Common categories include illicit drugs, counterfeit currencies, stolen data, hacking tools, and unlicensed pharmaceuticals. Additionally, there are markets for forged documents, firearms, and illegal surveillance equipment. The services offered extend to hacking and hacking consultation, money laundering, and even cybercriminal consulting. The diversity within the dark web market list underscores the broad spectrum of activity that exists within the dark web, reflecting both its complexity and the scale of underground trade that it facilitates.
Pricing, Quantity, and Shipping Information
The dark web market list is an essential resource for users seeking access to various online marketplaces operating within the hidden layers of the internet. These lists provide detailed information to help users navigate and make informed decisions about their transactions in these clandestine environments. One of the key features of a comprehensive dark web market list is the clear presentation of pricing details, enabling users to compare costs across different vendors and products. This transparency assists in finding the best deals and assessing the value of available items.
In addition to pricing, the market list offers crucial information about product quantities, allowing buyers to verify the available stock prior to making a purchase. This detail helps prevent misunderstandings around supply limitations and supports efficient purchasing decisions. Shipping information is another vital component, with the list providing insights into the shipping methods, expected delivery times, and whether discreet packaging is used to maintain anonymity. Such information is vital for ensuring privacy and security during the transaction process.
Overall, the dark web market list serves as a valuable tool by aggregating key data points—such as prices, quantities, and shipping options—so users can navigate complex marketplaces more confidently. Access to this organized information enhances the safety and efficiency of transactions, making it easier for users to find reliable vendors while maintaining their privacy and security.
COVID-19 Related Listings on DWMs
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the dark web has seen a surge in related listings, reflecting the increased demand for sensitive or illicit goods and services. Dark web market lists have become essential resources for navigating these hidden marketplaces, providing users with updated information on available items and vendors. These market lists serve as important tools for understanding the scope of COVID-19 related activities on the dark web and help users identify trustworthy sources within this concealed ecosystem. For those seeking more detailed information, exploring the dark web market list can offer comprehensive insights into current listings and trends, ensuring safer and more informed transactions in these confidential platforms.
Prevalence and Distribution
The prevalence and distribution of COVID-19 related listings on dark web markets have become an area of growing concern for authorities and cybersecurity experts. These listings often include counterfeit masks, unapproved vaccines, fraudulent testing kits, and other health-related products that exploit public fears during the pandemic. Dark web market lists serve as repositories for such illicit items, providing a platform for illegal transactions that can undermine public health efforts.
Analysis of dark web market lists reveals that COVID-19 related products are widespread, with their prevalence fluctuating based on current events and regulatory actions. Vendors frequently update their offerings to evade detection, making it challenging to monitor and control the distribution of these illegal items. Dark web market lists also indicate that these products are distributed across various regions, often tailored to meet specific demands in different countries.
The distribution of COVID-19 related listings on the dark web can be categorized into several key types:
- Counterfeit products, including masks, hand sanitizers, and testing kits
- Fake vaccination credentials or certificates
- Unapproved and potentially dangerous pharmaceuticals
- Unauthorized procurement of personal health information
- Illegal sale of COVID-19 related data and documentation
Dark web market lists highlight how these categories are interconnected, with vendors sometimes offering multiple related items to maximize profits. The presence of these listings underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and enforcement efforts to limit the availability of harmful COVID-19 related products. Understanding their prevalence and distribution through dark web market lists is crucial for informing strategies to protect public safety and combat illicit activities associated with the pandemic.
Main Product Categories During COVID-19
The dark web market list provides a comprehensive overview of various online marketplaces operating within the dark web, especially during challenging times such as the COVID-19 pandemic. These listings are crucial for understanding the landscape of illicit online activities, including the distribution of forbidden products and services. During the pandemic, many dark web markets adapted to new demands and challenges, leading to shifts in the main product categories offered on these platforms.
COVID-19 related listings on dark web market list saw an increase in health-related products, including counterfeit masks, PPE, and unregulated medications. Such items were often sought after due to supply shortages and rising demand. The main product categories during COVID-19 expanded to include not only health products but also digital goods and services, such as hacking tools and illicit software, which saw heightened activity amid the increased need for remote work and cybersecurity breaches.
On the dark web market list, illicit pharmaceuticals related to COVID-19, including unapproved remedies and supplements, comprised a significant portion of the offerings. Additionally, some marketplaces offered fake vaccination certificates or test results, highlighting a concerning trend during the pandemic. The main product categories during COVID-19 also encompassed financial fraud tools, such as phishing kits and stolen financial data, which became more prevalent as individuals and organizations faced cyber risks during this time.
Monitoring the dark web market list is vital for cybersecurity professionals and law enforcement agencies to gain insights into illicit trends related to COVID-19. Recognizing the shifts in main product categories during the pandemic helps target enforcement efforts and understand emerging threats. The dark web market list acts as a key resource to track these activities and mitigate associated risks effectively.
Most Common Items: PPE, Medicines, and Guides
The dark web market list often features a variety of COVID-19 related listings, reflecting the ongoing demand for essential health and safety products. Among the most common items found are personal protective equipment (PPE), medicines, and informational guides. These categories cater to individuals seeking to acquire critical supplies during the pandemic, often bypassing traditional channels.
On the dark web market list, PPE such as masks, gloves, and protective suits are highly prevalent. These items are in demand due to shortages and the desire for reliable protection, especially in regions with limited access to verified sources. Medicines, including antiviral drugs and other treatments, also appear frequently, although buyers should exercise caution when considering such offers, as authenticity and safety can’t always be guaranteed.
Additionally, guides related to COVID-19, including unofficial health information and test instructions, are available on the dark web market list. These guides often appeal to individuals seeking alternative or unverified advice during the pandemic. The presence of these listings underscores the dark web’s role as a hub for various COVID-19-related products and information, highlighting the importance of verifying sources and adhering to legal and health standards.
Examples of COVID-19 Specific Listings
COVID-19 related listings on dark web market lists have become a significant concern for cyber security and law enforcement agencies. These listings often include a variety of items and services that are directly tied to the pandemic, such as counterfeit personal protective equipment, unregulated medical supplies, and false documentation claiming COVID-19 testing or vaccination credentials. The dark web market list plays a pivotal role in tracking and understanding these illicit activities, offering a comprehensive overview of the different types of COVID-19 specific listings available to potential buyers or criminals.
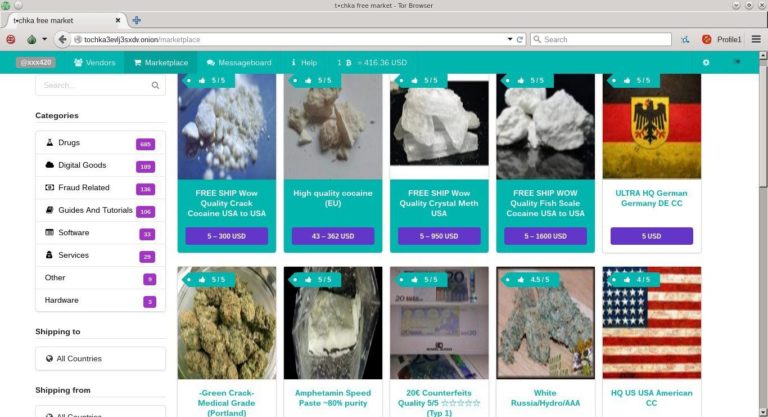
Examples of COVID-19 specific listings found on dark web market list include counterfeit masks, respirators, and gloves, which are sold at inflated prices due to high demand. Additionally, fraudulent COVID-19 test kits and vaccination certificates are frequently advertised to facilitate travel or employment requirements. Other listings may feature fake cures or unapproved pharmaceuticals claiming to cure or prevent COVID-19, posing serious health risks. The dark web market list serves as an essential resource to monitor such deceptive and illegal offerings, aiding authorities in identifying and disrupting these activities.
Monitoring the dark web market list that features COVID-19 related listings helps in understanding trends and the scale of illicit trade during the pandemic. This insight allows for better targeted enforcement actions and awareness campaigns. Recognizing common examples of COVID-19 specific listings enables officials and cybersecurity professionals to develop more effective strategies to combat these illegal sales and protect the public from scams, counterfeit products, and health hazards associated with the dark web market list.
Analysis of Dark Web Market Trends During Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted various aspects of society, including the dynamics of dark web markets. During this period, a noticeable shift in market activity and listings has occurred, reflecting changes in consumer demand, law enforcement efforts, and technological adaptations. Analyzing recent trends reveals how these markets have evolved, highlighting key players and emerging categories. The dark web market list serves as a crucial resource for understanding which platforms are currently active and prominent in this clandestine economy. One notable platform, which can be explored further, is available through the dark web market list, offering insights into the ongoing operations during the pandemic era. This analysis underscores the importance of continuous monitoring to grasp the shifting landscape of illicit online markets during these unprecedented times.
Temporal Evolution of Listings
The dark web market list has experienced significant shifts during the pandemic period, reflecting broader socio-economic and technological changes. These markets, which serve as anonymous platforms for buying and selling a variety of goods and services, have shown a notable increase in activity and diversification amidst the global health crisis. The temporal evolution of listings on these platforms reveals both resilience and adaptation in the face of increased law enforcement scrutiny and changing user behaviors.
During the initial stages of the pandemic, many dark web markets observed a surge in listings, particularly in areas related to health supplies, such as personal protective equipment and medicinal products. This spike was driven by heightened demand and supply chain disruptions in the physical market. As restrictions eased, the market list diversified further, incorporating a broader range of illicit goods, including digital goods and services. The analysis of market trends indicates that users and vendors have continuously adapted their offerings to exploit emerging opportunities while navigating increased enforcement activities.
The evolution of dark web market lists over time demonstrates a pattern of cyclical growth and contraction, often linked to external factors such as global crises, policy changes, and technological advancements. Market operators frequently modify their listings, protocols, and platform structures to evade detection and shutdowns. Consequently, the persistent presence of these markets underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and analysis to understand their impact on cybersecurity and law enforcement efforts.
Understanding the temporal trends in dark web market lists offers valuable insights into the shifting landscape of underground economies. It highlights the importance of collaborative efforts in cybersecurity and law enforcement to counteract illegal activities. As these markets continue to evolve dynamically, staying informed about their listings and operational tactics remains crucial for developing effective responses and policies.
Impact of Major COVID-19 Events on Listings
The dark web market list has experienced notable shifts during the COVID-19 pandemic, reflecting broader trends within underground economies. As the pandemic unfolded, various illicit marketplaces adapted to changing demand, law enforcement activity, and global circumstances, influencing the availability and type of listings. These changes have underscored the resilience and agility of dark web markets in response to major COVID-19 events.
During the early stages of the pandemic, there was a surge in listings related to health products, including counterfeit masks, PPE, and unauthorized pharmaceuticals. This spike was driven by increased demand for protective gear and medicines amid supply shortages. As a result, the dark web market list expanded to include more health-related illicit items, signaling an opportunistic shift by vendors and buyers seeking to capitalize on the crisis.
Following significant COVID-19 developments, such as lockdowns and economic disruptions, there was a noticeable decline in certain categories like stolen data and cybercrime services, possibly due to increased law enforcement monitoring and cyber vigilance. Conversely, drug listings within the dark web market list maintained steady volumes, with some categories even experiencing growth as traditional distribution channels were impacted by restrictions. This resilience highlights the adaptability of illegal markets in navigating pandemic-related hurdles.
The impact of major COVID-19 events also extended to payment methods and operational security. Vendors and buyers adapted by using cryptocurrencies and other anonymized payment systems to mitigate risks, which further influenced the composition of listings in the dark web market list. Overall, the pandemic has acted as both a catalyst and a disruptor, reshaping the landscape of illicit online marketplaces and emphasizing their capacity to evolve rapidly in response to global crises.
Price Fluctuations and Speculative Trends
The dark web market landscape has experienced significant shifts during the pandemic, reflecting broader social and economic disruptions. Analyzing dark web market lists reveals notable trends in the types of products and services in high demand, as well as fluctuations in pricing and market activity. These trends are indicative of changing consumer behaviors, increased demand for illicit goods, and the adaptations made by vendors to pandemic-related constraints.
Price fluctuations on the dark web often mirror supply chain disruptions and fluctuating demand for specific items. During the pandemic, certain categories such as pharmaceuticals, stolen data, and counterfeit goods saw a surge in popularity, which impacted their pricing strategies. For example, the cost of sensitive personal information and hacking tools has remained volatile, with occasional spikes during periods of heightened cybercrime activity. Conversely, some markets experienced a decline in overall transaction volume, likely due to increased law enforcement scrutiny and security measures.
Speculative trends within the dark web market list suggest a growing interest in emerging cybercriminal services, such as ransomware-as-a-service and deepfake content. Vendors are continuously innovating, offering more sophisticated tools and anonymization techniques to attract buyers. The dynamic nature of these markets makes them difficult to predict, but consistent analysis of the dark web market list provides valuable insights into ongoing shifts, potential risks, and opportunities for cybersecurity professionals.
Overall, the dark web market list serves as an important resource for understanding the continuous evolution of underground economies during the pandemic era. Monitoring these trends can aid in developing targeted strategies for disruption, awareness, and mitigation of illicit activities across digital platforms.
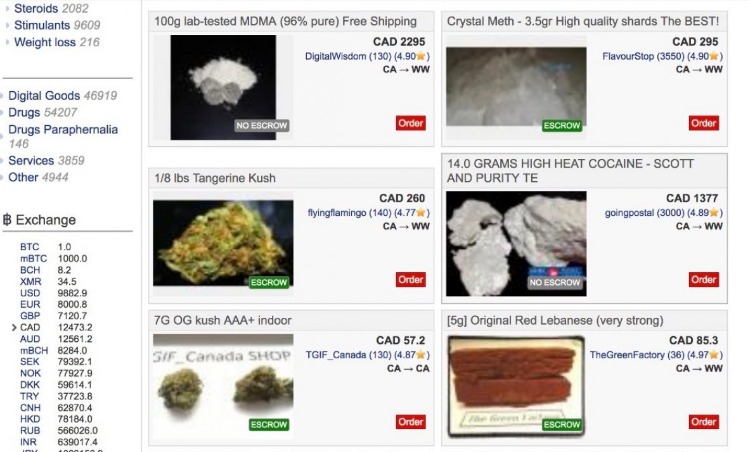
Vendor Behavior and Listing Diversity
The dark web market list has become an essential resource for understanding the evolving landscape of illicit online trading, especially during the pandemic period. Market trends during this time reveal significant shifts in vendor behavior and product offerings, influenced by changing societal needs and enforcement efforts. As the pandemic unfolded, many vendors adapted their strategies, leading to increased activity in certain sectors such as counterfeit goods, cryptocurrencies, and personal data. These shifts are reflected in the dark web market list, which documents emerging marketplaces and their unique listings, providing insight into the clandestine economy’s adaptability.
During the pandemic, vendors demonstrated heightened responsiveness to the demand for health-related products, including fake COVID-19 test kits and unapproved medications. This trend showcases the agility of vendors in exploiting current events, making the dark web market list a valuable tool for monitoring such developments. Additionally, the diversity of listings expanded as vendors diversified their offerings to include more advanced hacking tools, stolen financial information, and covert communication services. This diversification not only underscores the resilience of dark web ecosystems but also highlights the importance of vigilant monitoring to understand vendor behavior patterns over time.
The analysis of dark web market trends indicates a shift towards more sophisticated operations with increased emphasis on security and anonymity for vendors. Many newly established marketplaces emphasize encrypted payment methods and enhanced user privacy features, aiming to attract a broader vendor base and customer pool. The dark web market list reflects these trends by showcasing marketplaces that prioritize secure transactions and offer a wider variety of listings, which in turn indicates a maturing underground economy. Continual updates to this list serve as critical indicators for law enforcement and cybersecurity professionals seeking to comprehend and counteract illicit activities in these cyberspaces.
Market Responses to Public Attention and Media
Public attention and media coverage often influence the behavior and responses of dark web markets, shaping their operations and strategies in real-time. When a new crackdown or controversy emerges, these markets quickly adapt to maintain their presence and continue serving their users. Monitoring the dark web market list can offer valuable insights into ongoing trends, security measures, and the shifting landscape of illicit online activities. Staying informed about these developments is crucial for understanding how these hidden marketplaces operate within the broader ecosystem of online commerce.
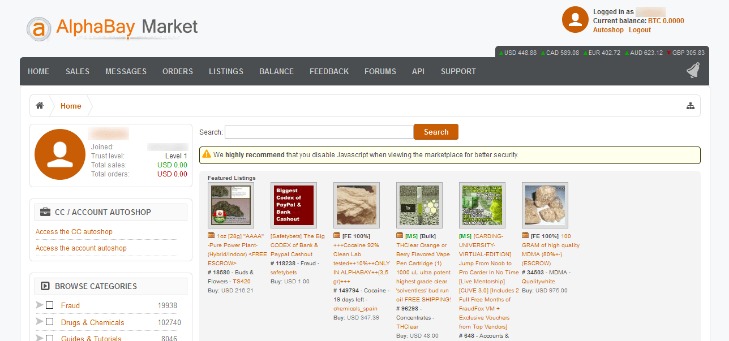
Correlation with Twitter and Wikipedia Activity
Understanding market responses to public attention and media coverage is crucial when analyzing the dynamics of dark web market lists. These underground marketplaces are often influenced by external stimuli such as news reports, social media activity, and online discussions, which can significantly impact user engagement and marketplace visibility. As public interest increases, so does the likelihood of increased activity on dark web market lists, reflecting heightened demand or scrutiny.
Research indicates a strong correlation between Twitter activity and fluctuations in interest surrounding dark web market lists. When news about certain illegal activities or market shutdowns trends on social media platforms, there is often a corresponding spike in searches and visits to these marketplaces. This real-time engagement can prompt rapid shifts in market behavior, leading to temporary surges or declines in activity.
Similarly, Wikipedia page views related to the dark web and its associated markets serve as an additional indicator of public awareness. Elevated Wikipedia activity around topics such as digital underground markets or cybercrime terminology often precedes or coincides with increased activity on dark web market lists. This suggests that informational searches drive users to explore these markets further, either to understand the risks or to locate specific marketplaces like the dark web market list.
In essence, the interplay between media attention, social media discourse, and informational resources like Wikipedia contributes to the evolving landscape of dark web markets. Monitoring these online signals can provide insights into the scale and direction of market activities, aiding in efforts to comprehend and, ultimately, counteract illicit online markets.
Response to Lockdowns, Waves, and Policy Changes
The dark web market list serves as a crucial resource for understanding the shifting landscape of online illicit trade and how markets respond to public attention and media coverage. When media outlets highlight certain dark web marketplaces, it often triggers a series of reactions within the ecosystem, including increased law enforcement activity and shifts in transaction patterns. These responses can lead to temporary closures or the emergence of new platforms, making the dark web market list a valuable tool for monitoring ongoing developments and identifying trends.
Public attention driven by media reports can influence the operational strategies of dark web markets, especially during significant events like lockdowns or policy changes. For instance, during lockdown periods, increased online activity and the heightened demand for certain goods may prompt dark web markets to adapt by expanding their product offerings or improving platform security measures. Conversely, heightened law enforcement scrutiny often results in marketplace shutdowns or the migration of users and vendors to less-visible networks, which are closely tracked via the dark web market list.
Wave patterns of activity in dark web markets often correlate with external factors such as policy shifts or major law enforcement crackdowns. During such waves, vendors and buyers tend to shift towards more clandestine platforms or transition to alternative currencies and anonymization methods. The dark web market list plays an essential role in documenting these transitions by providing updated information about active marketplaces and their statuses, helping analysts and security professionals understand the resilience and adaptability of these illicit networks.
Ultimately, the dynamic responses of dark web markets to public scrutiny, policy changes, and external disruptions demonstrate their capacity to adapt and survive amidst ongoing enforcement efforts. Regularly updated resources like the dark web market list are indispensable for tracking these changes, providing insights into emerging threats, and aiding efforts to combat illegal online activities. By monitoring these responses, stakeholders can better anticipate future trends and develop more effective strategies for disruption and prevention.
Public Attention’s Effect on Listing Volume and Types
Public attention and media coverage play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of dark web markets, influencing both their visibility and the types of listings available. When a dark web market garners widespread media interest, it often experiences a surge in user traffic and listing activity, as individuals become more aware of its existence. This heightened awareness can lead to increased transaction volume, particularly for high-demand categories such as illicit drugs, stolen data, or counterfeit items. Additionally, media focus can impact the perceived legitimacy and safety of a dark web market, encouraging new vendors to join or existing vendors to expand their offerings.
The response of a dark web market to public attention can be multifaceted. Market operators might adjust their policies or diversify their listings to capitalize on the publicity, introducing new product categories or enhancing security measures to build trust among users. Conversely, intense media scrutiny can also attract law enforcement attention, prompting market shutdowns or the relocation of operations. The dark web market list serves as a valuable resource in tracking these shifts, revealing which platforms gain popularity rapidly and how their listings evolve in response to public and media interest.
As public attention increases, the volume and types of listings tend to change in predictable ways, such as:
- Boost in the number of illicit substance listings as vendors attempt to meet rising demand.
- More vendors and buyers participating, creating a more diverse and competitive marketplace.
The ongoing interaction between public attention, media coverage, and the dark web market list highlights the importance of understanding these market responses. Vendors and buyers alike adapt their strategies based on perceived risks and opportunities, which directly influence the overall landscape of illegal online marketplaces.
Marketplace Dynamics and Vendor Behavior
Marketplace dynamics and vendor behavior play a crucial role in shaping the ecosystem of underground markets, especially within the dark web. These markets operate through complex networks where vendors compete for trust and reputation, often adapting their strategies to navigate law enforcement efforts and customer demands. Understanding the patterns of vendor activity and the overall market structure provides insight into how illicit goods and services are exchanged in these hidden marketplaces. A comprehensive dark web market list can serve as a valuable resource for analyzing vendor trends, product availability, and market longevity, offering a window into the shadow economy’s evolving landscape.
Vendor Distribution and Listing Power Law
The landscape of the dark web market list is shaped by complex marketplace dynamics and vendor behaviors that influence overall activity and trustworthiness. Understanding how vendors operate and distribute their products is crucial for analyzing these underground markets. Vendors often adapt their strategies based on market demand, law enforcement activity, and competition, creating a constantly evolving environment. This environment is characterized by specific patterns of vendor distribution and the application of the vendor power law, which describes the imbalance where a small number of vendors account for a large portion of sales or listings.
Within dark web markets, vendor behavior plays a pivotal role in shaping the ecosystem. Vendors with high listing power tend to dominate the market, attracting more buyers through reputation and consistent delivery. The distribution of these vendors typically follows a power law, meaning a few vendors hold a majority of the market share while most have limited listings. This skewed distribution impacts market stability and trust, as buyers are more likely to purchase from well-established vendors.
Vendor distribution in dark web marketplaces often aligns with the vendor power law, which can be summarized as:
- The top vendors: These vendors hold extensive listings and secure a significant market share. Their reputation is built over time through consistent and reliable service, making them popular among buyers seeking safe transactions.
- The mid-tier vendors: These providers have a moderate number of listings and are often competing for visibility. Their reliability can vary, and their market share is smaller compared to the top tier.
- The small vendors: Many vendors enter the market with limited listings, often trying to establish their reputation. They have minimal influence on overall market dynamics but contribute to the diversity of offerings on the dark web market list.
- Hacked VPN log-ins were disproportionately popular on Russian markets, which accounted for 43% of all VPN listings.
- ExpressVPN and Windscribe were the next most frequently listed VPN services on Kraken.
- Over a third (35%) of the 148 listings in this category were for these four platforms, which was an outsize proportion given we found account details for 36 learning platforms in total.
- The following table shows which categories of hacked account credentials were most popular on the darknet markets.
- None of the darknet markets we looked at in our previous report still operate in 2023.
- These listings were observed 9464 times during this period, allowing us to investigate their temporal evolution.
This vendor distribution pattern is vital for understanding market resilience and susceptibility to disruption. It emphasizes the importance for buyers to rely on trusted and established vendors and for analysts to monitor vendor behavior patterns to gauge market health. The dark web market list serves as a critical resource in tracking these vendors, highlighting the ongoing shifts in vendor positions and the emergence of new players in the underground economy. Recognizing the vendor power law helps in predicting market trends and understanding the potential risks associated with emerging vendors versus established ones.
Vendor Specialization and Diversity
The dark web market list comprises a complex ecosystem where vendors operate with varied strategies, specialization, and diversity. Understanding marketplace dynamics and vendor behavior is essential for grasping how illicit transactions and exchanges occur within these hidden environments. Vendors on the dark web often adapt their practices to meet the fluctuating demands of their clientele, making the landscape highly fluid and unpredictable.
Vendor behavior on dark web markets is influenced by multiple factors, including the level of trust within the community, the type of products or services offered, and the reputation they establish over time. Vendors may specialize in specific product categories such as drugs, compromised data, counterfeit documents, or hacking services. Others diversify their offerings to maximize revenue and reduce dependency on a single niche. This diversity within the dark web market list enhances the resilience of these markets while complicating efforts to regulate or shut them down.
Marketplace dynamics are shaped by both vendor strategies and buyer preferences. Vendor reputation systems, feedback, and escrow services help build trust, encouraging ongoing transactions. Some vendors become prominent figures within the dark web community due to their consistent quality and reliability, which can influence market stability. Conversely, vendors who fail to maintain quality or deceive buyers risk losing credibility, thus affecting their standing within the dark web market list.
- Market Specialization: Vendors focus on specific niches to cater to targeted audiences, establishing expertise and loyalty.
- Diversity: A wide range of products and services are offered, reflecting the varied demands of dark web consumers.
- Reputation Management: Trust and reputation are critical, with vendors actively managing feedback and customer relationships.
- Innovation and Adaptation: Vendors frequently modify their practices to evade law enforcement detection and meet evolving marketplace needs.
- Market Listings: The dark web market list consolidates vendors by category, helping buyers identify reliable sources and risky providers alike.
In summary, the dark web market list illustrates a vibrant ecosystem characterized by diverse vendor behaviors and marketplace dynamics. Vendors’ strategic specialization and diversification play a pivotal role in shaping the resilience and evolution of these clandestine markets. Monitoring and understanding these patterns are crucial for efforts aimed at combating illegal activities on the dark web.
Communication Methods and Seller Trust
The dark web market list plays a crucial role in understanding the complex ecosystem of clandestine online trading. These markets operate in a gray area of the internet, where vendors and buyers interact under varying levels of anonymity and trust. Analyzing marketplace dynamics and vendor behavior offers insight into how these illicit markets function and evolve over time. The dark web market list serves as a reference point for identifying active markets and monitoring shifts in vendor practices and platform stability.

Communication methods between buyers and vendors on dark web markets are primarily based on secure messaging systems that prioritize privacy and confidentiality. These platforms often implement encrypted communication channels, escrow services, and anonymized profiles to build confidence among participants. Vendor behavior in such environments is heavily influenced by the need to maintain reputation, avoid law enforcement, and ensure consistent sales. Successful vendors tend to be responsive, discreet, and transparent about their offerings within the confines of the market rules, fostering a sense of trust despite the illegal nature of transactions.
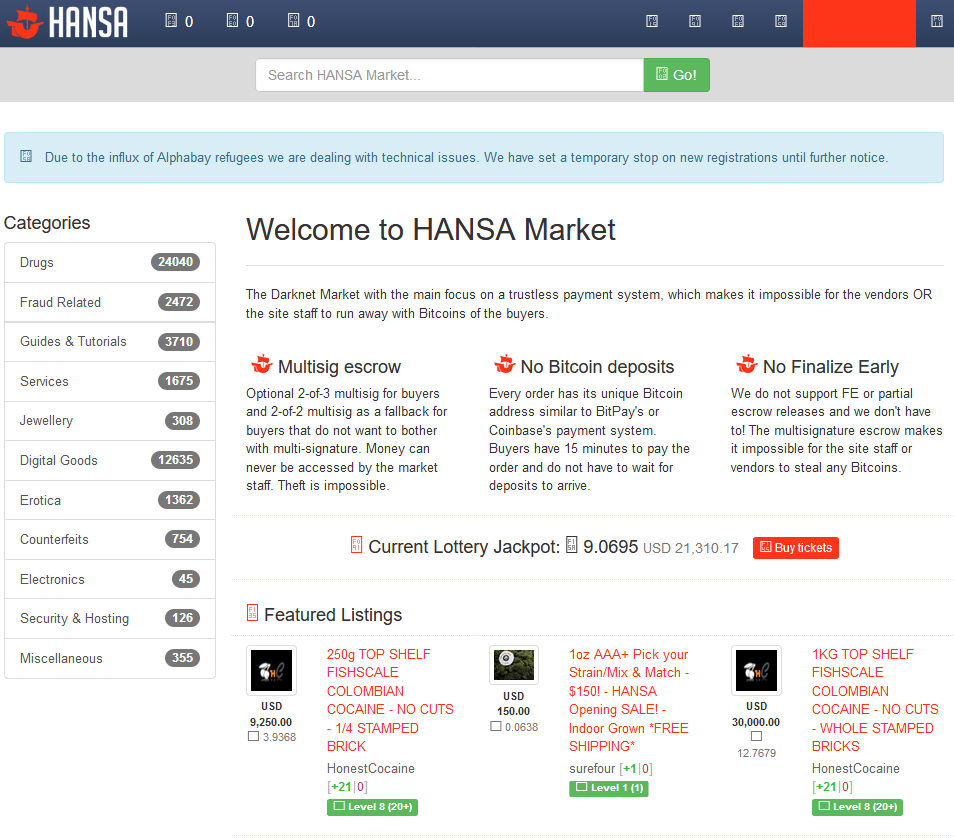
Seller trust plays a vital role in the sustainability of dark web marketplaces. Due to the anonymous environment, reputation systems, feedback, and escrow services are critical in establishing reliability. Vendors who consistently deliver quality products and communicate effectively are more likely to earn positive reviews, increasing their credibility among buyers. Conversely, suspicious or unreliable vendors risk losing trust and being expelled from the marketplace, which can significantly impact their sales volume. The dark web market list often highlights the most reputable vendors, providing buyers with guidance and helping to reduce the risks associated with illicit trade.
Case Studies of Highly Active Vendors
The landscape of dark web markets is constantly evolving, driven by complex marketplace dynamics and diverse vendor behaviors. Understanding these elements is essential for assessing the overall security, reliability, and risks associated with these clandestine platforms. Highly active vendors play a critical role in shaping market trends, influencing buyer confidence, and maintaining the flow of illicit goods and services. Analyzing case studies of such vendors provides insights into their strategies, operational models, and factors that contribute to their sustained activity over time.
One notable aspect of dark web market list entries is the prominence of vendors who consistently rank as top sellers. These vendors often demonstrate high responsiveness, maintain consistent quality, and employ secure transaction methods to cultivate buyer trust. Their behavior can include rapid response to inquiries, establishing reputation through reviews, and diversifying product offerings to adapt to market demand. For example, some vendors focus on niche markets, capitalizing on specialized product categories that experience increased demand, thereby cementing their status within the dark web marketplace ecosystem.
Case studies of highly active vendors reveal common traits such as strategic pricing, effective marketing within the dark web community, and robust logistics networks. Their reputation is often enhanced through deliberate engagement with the community, use of trust-building mechanisms, and discreet communication channels. These vendors tend to be adaptable, quickly shifting their practices in response to law enforcement actions or market fluctuations, which underscores the resilience and agility required to sustain long-term activity.
The dark web market list commonly highlights vendors who exhibit exceptional operational efficiency—minimizing delays, managing inventories effectively, and handling disputes professionally. Their consistent presence on the market not only boosts their sales volume but also influences overall market dynamics, such as pricing trends and product availability. Understanding their behaviors provides valuable insights for law enforcement agencies, cybersecurity professionals, and market participants aiming to mitigate risks associated with illicit activities.
In conclusion, the success of highly active vendors within the dark web market list underscores the importance of analyzing vendor behaviors and marketplace interactions. Their strategies and operational models significantly impact the stability, integrity, and evolution of dark web markets, making them key focal points for ongoing research and law enforcement efforts to combat illegal activities conducted through these clandestine platforms.
Challenges in Monitoring and Data Collection
Monitoring and data collection within the dark web market landscape pose significant challenges due to its inherently secretive and dynamic nature. The anonymity provided by encrypted networks complicates efforts to track transactions, identify participants, and gather reliable intelligence. This makes it difficult for analysts to maintain accurate and up-to-date information, especially when dealing with constantly shifting marketplace structures. A comprehensive dark web market list is essential for researchers and security professionals aiming to understand illicit trade networks, but compiling and verifying such data remains a complex task. For those interested in exploring current dark web markets, reputable directories like the dark web market list provide valuable insights into ongoing activities and emerging platforms.
Technical Difficulties and Protective Measures by DWMs
Managing and maintaining an accurate dark web market list presents significant challenges in monitoring and data collection. Due to the inherently clandestine nature of the dark web, gathering reliable and comprehensive data requires sophisticated techniques and persistent efforts. Dark web marketplaces frequently change domains, employ advanced anonymization methods, and utilize encrypted communications, making it difficult for analysts to track consistent patterns or identify all active marketplaces effectively. This dynamic environment complicates efforts to compile an up-to-date dark web market list that reflects current activities accurately.
One of the primary technical difficulties in monitoring these markets is the need for specialized tools and expertise to navigate the dark web securely. Automated scraping tools must be carefully designed to avoid detection and blocks by marketplace administrators. Additionally, data collection often faces issues such as incomplete information, inconsistent data formats, and potential data contamination from false listings or scams. These factors hinder the creation of reliable analytics and can impede timely responses to emerging threats or illegal activities associated with dark web markets.
Protective measures by Dark Web Market (DWM) operators further complicate efforts to monitor these sites effectively. Many operators implement defensive mechanisms like CAPTCHAs, geo-blocking, and sophisticated encryption to deter automated data collection. They also frequently update their site structures and employ anti-bot technologies to thwart tracking attempts. To mitigate these challenges, security teams often adopt layered strategies, including human intelligence, undercover operations, and collaboration with law enforcement agencies, all aimed at increasing the accuracy of the dark web market list while ensuring their own operational safety.
Automated Crawling and Data Annotation Limitations
Monitoring and data collection on the dark web market list present significant challenges due to the inherently secretive and dynamic nature of these marketplaces. These platforms are often designed to evade detection through encryption, anonymization techniques, and rapid site changes, making it difficult for researchers and law enforcement agencies to maintain reliable data streams. Automated crawling processes struggle to keep pace with the frequent updates, closures, and emergence of new markets, leading to gaps in the data collected and potential inaccuracies. Furthermore, the complexity of extracting meaningful information amidst obfuscated content complicates efforts to compile comprehensive and up-to-date dark web market lists.
Automated crawling technologies are limited by their ability to adapt to the evolving structures of dark web marketplaces. These sites frequently employ anti-crawling measures, such as CAPTCHAs, dynamic content loading, and deliberate site reconfiguration, which hinder the ability of traditional bots to access and extract data efficiently. Additionally, the inconsistent formats and lack of standardization across different platforms exacerbate these issues, resulting in incomplete or unreliable datasets for analysis.
Data annotation, crucial for organizing and analyzing dark web market information, faces its own limitations. Manual annotation is labor-intensive and prone to human error, while automated annotation tools often misinterpret complex or encrypted content, leading to inaccuracies. These limitations affect the quality of insights derived from the dark web market list, impacting efforts to understand vendor behaviors, product categories, and transaction patterns. Overcoming these challenges requires innovative approaches that combine advanced machine learning techniques with specialized tools designed to operate within the unique environment of the dark web.
Data Biases and Language Limitations
Monitoring and data collection within dark web markets present unique challenges due to the clandestine nature of these platforms. The encrypted and anonymous environment makes it difficult for researchers and security professionals to gather accurate and comprehensive data. This becomes especially crucial when compiling a dark web market list, as incomplete or unreliable information can hinder threat assessment and response strategies.
One of the primary issues faced is the dynamic and volatile landscape of these markets. New platforms frequently emerge while existing ones may shut down without notice, complicating efforts to maintain an up-to-date dark web market list. Additionally, the use of various encryption techniques and the Tor network further complicate data collection efforts, often leading to gaps and inconsistencies in the data gathered.
Data biases also pose significant challenges. Since much of the information is collected manually or through limited automated tools, there can be a skew towards more visible or larger marketplaces, leaving smaller or less active ones underrepresented. This bias can distort perceptions of activity levels and the overall scope of illicit operations on the dark web.
Language limitations are another critical factor impeding effective monitoring. Many dark web markets operate in multiple languages, and language barriers can prevent accurate data extraction and interpretation. Automated translation tools may not always capture contextual nuances, leading to misunderstandings or misclassifications of market activities. This is especially problematic when compiling a comprehensive dark web market list that aims to cover various linguistic regions.
In summary, overcoming challenges in monitoring, data collection, and addressing biases and language limitations is essential for maintaining an accurate and current dark web market list. This helps law enforcement, cybersecurity experts, and researchers better understand the scope of illicit activities and develop effective countermeasures.
Implications for Public Health and Policy
The dark web market list refers to a compilation of online marketplaces that operate within the hidden layers of the internet, often facilitating illicit activities. As these markets continue to grow and evolve, they present significant implications for public health and policy. The anonymity and scale of dark web markets make it challenging for authorities to monitor and regulate the trade of illegal substances, counterfeit goods, and other prohibited items. Understanding the structure and function of the dark web market list is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat illegal activities and protect public well-being. Policymakers must consider the risks associated with these clandestine markets to formulate appropriate legal frameworks and enforcement mechanisms.
Risks of Illicit COVID-19 Product Trade
The existence of dark web markets, particularly those listing illicit COVID-19 products, presents significant implications for public health and policy. These marketplaces facilitate the trade of falsified or unregulated medical supplies, including counterfeit vaccines, unverified treatments, and fake testing kits. Such products pose serious health risks to individuals and communities by undermining efforts to control the pandemic and potentially exposing users to dangerous substances. The dark web market list provides a curated overview of these illicit platforms, highlighting the scope and scale of illegal operations related to COVID-19. Policymakers must understand these threats to develop targeted strategies for monitoring and shutting down such markets, thereby reducing the spread of unsafe products that could worsen public health outcomes.
Additionally, the trafficking of illicit COVID-19 products on dark web markets complicates international efforts to regulate health supplies and enforce safety standards. The anonymous nature of these platforms makes it challenging for authorities to trace transactions and identify vendors, increasing the risk of widespread distribution of harmful substances. This clandestine trade not only endangers individual consumers but also undermines public trust in legitimate healthcare systems. To combat this, integrated approaches combining law enforcement, cyber surveillance, and public awareness campaigns are essential. Regularly updated dark web market list reports can serve as valuable tools for agencies aiming to track and dismantle illegal networks engaged in the trade of contaminated or counterfeit COVID-19 products, ultimately safeguarding public health priorities and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Effectiveness of Law Enforcement Strategies
The proliferation of dark web markets has significant implications for public health and policy, demanding careful consideration from authorities and stakeholders. These hidden marketplaces facilitate the trade of illegal substances, counterfeit goods, and other illicit items, which can directly impact societal well-being. The presence of a comprehensive dark web market list highlights the extent and variety of these illegal platforms, posing challenges for regulation and enforcement efforts. Consequently, public health initiatives must adapt to mitigate the harms associated with illegal drug distribution and other illicit activities originating from these markets.
Law enforcement strategies aimed at dismantling dark web markets often involve technological investigations, infiltration, and cooperation across borders. The effectiveness of such strategies varies depending on resource allocation, technological capabilities, and international cooperation. Targeted operations that focus on high-traffic or high-volume markets have shown some success in reducing the availability of illicit goods. However, the adaptability of dark web vendors and the frequent emergence of new platforms listed in sources like the dark web market list complicate these efforts. Overall, while law enforcement can disrupt certain markets temporarily, creating sustainable solutions requires a multifaceted approach integrating technological, legal, and public health policies.
Policy measures must also address underlying social and economic factors that facilitate participation in dark web markets. This includes improving access to healthcare, mental health services, education, and economic opportunities, which can reduce demand and supply sides of illegal trade. International collaboration and updated legal frameworks are essential to keep pace with the evolving digital landscape. Ultimately, a balanced approach that combines law enforcement, harm reduction, and social support systems is vital to effectively address the complex challenges posed by dark web markets and to protect public health on a broader scale.
Recommendations for Continuous Monitoring
The emergence of dark web market lists presents significant implications for public health and policy, necessitating a strategic approach to mitigate associated risks. These market lists often serve as platforms for illegal activities, including the distribution of illicit pharmaceuticals, arms, and counterfeit products, which can have detrimental effects on community safety and individual well-being. Public health agencies must recognize the potential for these markets to facilitate the spread of dangerous substances and take proactive measures to monitor and respond to such threats. Robust policies should aim to block access, track illicit transactions, and educate the public on the dangers associated with illegal online marketplaces.
Given the constantly evolving nature of dark web market lists, continuous monitoring becomes essential to staying ahead of emerging trends and criminal operations. Implementing advanced cybersecurity measures, AI-powered surveillance tools, and real-time data analysis can enhance the ability of authorities to detect and dismantle illicit networks. Collaboration across international agencies, tech companies, and law enforcement organizations is crucial for effective intelligence sharing and coordinated responses. Regular updates and assessments of emerging dark web market lists can provide valuable insights into shifting patterns, enabling policymakers to adapt strategies accordingly.
Moreover, fostering public awareness and education about the risks linked to unauthorized online markets can reduce demand and prevent vulnerable populations from exploitation. Policies should also promote transparency, accountability, and strong legal frameworks to deter illicit activities and protect public health. Overall, a proactive, integrated approach to monitoring and addressing dark web market lists is vital for safeguarding communities and reducing their impact on national and global security.
Future Directions and Research Opportunities
The existence and operation of dark web market lists have significant implications for public health and policy. These marketplaces often facilitate the trade of illicit substances, counterfeit medications, and other harmful products, posing direct risks to individual health and community well-being. Monitoring and understanding these dark web market lists enable public health officials to better assess emerging threats, model the spread of illegal substances, and develop targeted interventions. Furthermore, law enforcement agencies can utilize insights from these lists to dismantle networks involved in criminal activities, thereby reducing the circulation of dangerous goods. The proliferation of dark web market lists underscores the need for robust policies that address cybersecurity vulnerabilities, enhance legal frameworks, and promote cross-sector collaboration.
Looking ahead, future research opportunities lie in developing sophisticated analytical tools capable of real-time monitoring of dark web market lists. Advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence can aid in identifying trends, detecting new substances, and predicting market shifts before they impact public health. Additionally, interdisciplinary research integrating criminology, data science, and public health can shed light on the socio-economic factors driving participation in these markets. Enhancing transparency and sharing intelligence regarding dark web market lists can also foster better international cooperation and policy responses. Ultimately, ongoing research and adaptive policies are essential to mitigate the risks associated with these covert online platforms and safeguard public health.