Overview of Dark Markets
Dark markets, also known as dark web marketplaces, are digital platforms that operate on the part of the internet not indexed by traditional search engines. These clandestine markets facilitate the exchange of goods and services that often involve illegal activities, including the sale of illicit drugs, weapons, stolen data, and counterfeit items. Due to their hidden nature, access to dark markets requires specialized software and configurations that ensure user anonymity and privacy. For those interested in exploring this shadowy ecosystem, resources like darkmarkets provide insights into their structure and operations. Understanding dark markets is essential for cybersecurity professionals, policymakers, and researchers aiming to combat cybercrime and protect digital infrastructure. While these platforms pose significant challenges, ongoing efforts to monitor and regulate activity on dark markets remain crucial in maintaining online security and order.
Definition and Composition of Dark Markets
Dark markets, also known as dark web marketplaces, are online platforms that facilitate the anonymous exchange of goods and services. These markets operate on the dark web, a segment of the internet that is not indexed by standard search engines and requires specialized software, such as Tor, for access. Due to their hidden nature, dark markets are often associated with illicit activities, including the trade of illegal drugs, weapons, counterfeit documents, and stolen data. Understanding the composition and definition of these markets is essential for grasping their role within the broader landscape of the internet.
Dark markets are typically composed of various components that enable secure and anonymous transactions. These components include:
- Marketplaces: Dedicated websites where vendors list their products and buyers browse offerings. These sites often feature escrow services to ensure transaction safety.
- Cryptocurrency Payment Systems: Most transactions are conducted using cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to maintain anonymity and prevent traceability.
- Vendor and User Accounts: Participants create profiles that sometimes include reputation ratings, reviews, and feedback to build trust within the community.
- Encryption and Anonymity Tools: Technologies such as Tor and PGP encryption protect user identities and secure communications.
- Escrow and Dispute Resolution Services: Mechanisms to hold funds during transactions and resolve disagreements, minimizing risks for buyers and sellers.
The definition of dark markets centers on their function as clandestine hubs for anonymous exchange, often characterized by their resilience and adaptability. They form a complex ecosystem driven by the need for privacy and security, making them a significant component of the broader dark web. While many utilize such markets for illegal purposes, some legitimate actors also use them to operate securely within sensitive industries. Recognizing the composition and the underlying architecture of these platforms is crucial for understanding their impact on digital security and law enforcement efforts.
Types of Dark Trading Venues
Dark markets are hidden online marketplaces that operate outside the reach of conventional internet visibility, often used for trading a wide range of goods and services. These marketplaces function on anonymized networks and employ specialized domain structures, making them difficult to detect and regulate. The primary purpose of dark markets is to facilitate transactions that users prefer to keep private or that are illegal in certain jurisdictions.
There are various types of dark trading venues, each designed to cater to different user needs and types of transactions. Some of the most common include cryptocurrency-based marketplaces, where digital currencies like Bitcoin are used for anonymous transactions. These platforms often feature encrypted communication and escrow services to ensure user safety and transaction security. Another type comprises more traditional black markets that specialize in illegal goods and services, often hidden within the deep web or dark web, accessible via Tor browsers and other anonymity-preserving tools.
Dark markets and other dark trading venues pose unique challenges for law enforcement and regulatory authorities, as they enable illegal activities such as drug trafficking, weapon sales, and counterfeit goods. Despite efforts to shut them down, they continually evolve with new technologies and security measures. Users engaging with these platforms should be aware of the inherent risks and legal implications involved, given the clandestine nature of dark markets and the potential for exploitation or loss.
Participants in Dark Markets
Dark markets, also known as dark web marketplaces, are hidden online platforms that facilitate the exchange of goods and services outside the reach of conventional internet search engines and regulatory oversight. These markets operate on encrypted networks, often using anonymizing technologies to protect the identities of both buyers and sellers. They are popular for trading a variety of items, some of which are illegal or heavily regulated in many jurisdictions.
Participants in dark markets include a diverse range of individuals and entities, each with different motivations and levels of involvement. Criminal actors make up a significant portion of participants, engaging in the sale of illicit goods such as drugs, stolen data, weapons, and counterfeit currency. These actors rely on the anonymity and security features of dark markets to conduct transactions with reduced risk of detection.
However, not all participants are involved in illegal activities. Some users access dark markets for privacy reasons, seeking to buy or sell items that are legal but require confidentiality. Additionally, hackers and cybercriminal groups extensively use these platforms to distribute malware, sell hacking services, or trade sensitive information. Law enforcement agencies also monitor and investigate dark markets to combat criminal enterprises and dismantle illegal networks.
- Buyers and Sellers: The primary participants, engaged in trading various goods and services, ranging from legitimate to illegal.
- Market Operators: Administrators who manage the platform infrastructure, enforce rules, and facilitate transactions.
- Law Enforcement: Agencies working to identify and apprehend individuals involved in illegal activities within these platforms.

The ecosystem of dark markets illustrates a complex environment where anonymity and clandestine communication play central roles, making them a significant challenge for regulation and law enforcement efforts. Understanding the different types of participants helps in developing strategies to address the risks associated with these hidden online marketplaces.
Key Metrics and Indicators in Dark Markets
Dark markets operate in the shadows of the internet, presenting unique challenges in measuring their activity and understanding their scope. Key metrics and indicators are essential for analyzing these clandestine marketplaces, helping researchers and law enforcement identify patterns, trends, and potential risks. By monitoring transaction volumes, user activity, and product listings, stakeholders can gauge the scale and evolution of dark markets. A vital source of information can be found by exploring various *darkmarkets*, which often serve as hubs for illicit trading and provide insights into the behind-the-scenes economy on the dark web. Understanding these key metrics not only aids in the development of effective strategies to combat illegal activities but also enhances awareness of how these covert markets operate and evolve over time.
Market Dynamics and Behavioral Insights
Understanding market dynamics and behavioral insights is essential for analyzing complex economic environments, especially within the shadowy realms of darkmarkets. These platforms operate outside conventional legal frameworks, where unique behaviors and rapid shifts in supply and demand significantly influence market flow. By examining consumer and vendor actions, as well as the underlying psychological factors at play, we gain a deeper appreciation for the forces driving these clandestine economies. Diverse factors such as trust mechanisms, reputation systems, and risk perception shape interactions in darkmarkets, making them a compelling subject for behavioral analysis and economic study. Exploring these aspects can offer valuable insights into how illicit markets adapt and evolve in response to law enforcement efforts and technological advancements. For more detailed exploration, consider researching darkmarkets.

Trading Volume and Liquidity in Dark Pools
Dark markets, also known as dark pools, play a significant role in modern financial trading by providing a private arena for large-scale transactions outside traditional exchanges. Understanding the market dynamics and behavioral insights that influence these platforms is crucial for investors and market participants. These hidden trading environments impact overall liquidity, trading volume, and market stability, shaping the broader financial landscape.
Market dynamics within dark pools are characterized by a unique set of factors that differ from conventional exchanges. These include the preferences of high-frequency traders, institutional investors, and other large market participants seeking anonymity and reduced market impact. Behavioral insights reveal that traders often prefer dark pools to mitigate the risk of information leakage, which can adversely affect prices in public markets.
The trading volume in dark markets tends to be substantial, especially for securities that are subject to large block trades. Increased trading activity in these private venues can influence the overall liquidity of the markets, often leading to more efficient price discovery in the broader financial system. However, the lack of transparency can also pose challenges in assessing the true market depth and activity levels.
Liquidity in dark pools is a double-edged sword: while they can offer enhanced liquidity for large trades without moving the market significantly, they may also contribute to fragmentation of liquidity across multiple venues. This fragmentation can impact the execution quality and the transparency of real-time trading data, making it harder for traders to gauge the true market conditions.
- Market participants utilize dark markets to execute large orders discreetly, reducing their market impact and potential price slippage.
- Behavioral factors, such as the desire for anonymity and minimization of information asymmetry, drive traders toward dark pools.
- Liquidity levels in dark pools influence overall market stability; insufficient liquidity can lead to increased volatility.
- Trading volume growth in dark markets reflects a shift toward private trading venues, affecting the transparency of the broader financial ecosystem.
Overall, dark markets are an integral part of the modern trading environment, governed by complex market dynamics and behavioral insights. While they offer advantages in terms of confidentiality and liquidity for large trades, their influence on market transparency and stability continues to evolve, making them a critical focus for regulators and market participants alike.
Price Discovery and Price Impact
Market dynamics within darkmarkets are shaped by unique factors that distinguish them from traditional financial environments. These clandestine platforms operate outside the reach of standard regulations, creating a landscape where supply and demand are influenced by anonymity, perceived security, and the availability of illicit goods and services. Behavioral insights reveal that participants in darkmarkets often exhibit risk-averse tendencies, yet they are driven by the promise of privacy and access to hard-to-find items, which can significantly impact trading volume and market stability.
Price discovery in darkmarkets occurs through complex interactions among buyers and sellers who rely heavily on trust, reputation, and encrypted communication channels. Unlike traditional markets, where transparent pricing mechanisms facilitate efficient price discovery, darkmarkets depend on reputation systems, negotiation, and sometimes automated trading bots to determine fair values. Consequently, prices tend to fluctuate based on the perceived reliability of sources, scarcity of products, and prevailing levels of demand, which can sometimes lead to volatile price movements.
The concept of price impact is also crucial in understanding darkmarkets. Large trades or sudden spikes in demand can cause significant deviations from established price levels, influencing not only individual transactions but also the broader market sentiment. Because of the anonymous nature of these platforms, assessing market depth and liquidity becomes challenging, often amplifying the effects of large transactions. Navigation within darkmarkets requires participants to remain vigilant about these price impacts, as they can swiftly alter trading conditions and influence the overall stability of these unregulated environments.
Market Transparency and Information Asymmetry
Dark markets, often characterized by their clandestine operations and anonymity, play a significant role in shaping market dynamics and behavioral insights within illicit economies. These underground marketplaces create unique environments where traditional market forces are influenced by clandestine factors, leading to distinct patterns of supply and demand. Participants often rely on trust mechanisms and reputation systems that differ markedly from those in open markets, affecting consumer behavior and seller strategies.
Understanding market transparency and information asymmetry is crucial when analyzing dark markets. Due to their secretive nature, these platforms inherently operate with high levels of information asymmetry, where buyers often lack full knowledge about the quality, authenticity, or legitimacy of products and services. This information gap can lead to increased risks of fraud and deception, compelling participants to develop specialized tactics for verification and trust-building.
The existence of dark markets significantly alters traditional market dynamics by enabling anonymous transactions that are not easily monitored or regulated. This environment fosters a degree of resilience for illicit activities, as traders and consumers navigate complex layers of encryption and obfuscation to conduct exchanges. Recognizing these factors is essential to understanding how dark markets influence broader economic and social systems, as well as the behavioral patterns that sustain them.
Addressing the challenges posed by dark markets requires a deep understanding of the underlying market forces and the behavioral incentives driving participants. By examining how transparency and information asymmetry shape decision-making processes, stakeholders can better strategize efforts to combat illegal activities while acknowledging the sophisticated mechanisms that support these clandestine platforms.
Risks and Challenges in Dark Markets
Engaging with darkmarkets presents a unique set of risks and challenges for individuals and entities involved in these hidden online environments. Due to their anonymous nature and unregulated operations, participants often face issues related to security, legality, and operational reliability. The prominence of criminal activities within darkmarkets amplifies concerns about scams, fraud, and law enforcement intervention. Navigating this underground economy requires careful consideration of the unpredictable legal landscape and the potential for financial loss. For those interested in understanding more about the inner workings and risks associated with darkmarkets, exploring dedicated resources can provide valuable insights and cautionary advice.
Regulatory Concerns
Dark markets, often associated with illicit activities and illegal transactions, present a complex landscape filled with significant risks and challenges. Participants in these markets face heightened security threats, including hacking, scams, and theft, which can lead to considerable financial loss. Additionally, the clandestine nature of dark markets makes it difficult to verify the legitimacy of vendors and transactions, increasing the potential for fraud.
One of the primary concerns surrounding dark markets is the ever-present threat of law enforcement intervention. Authorities worldwide are actively monitoring and taking action against illegal activities conducted on these platforms, leading to unpredictable legal consequences for users engaged in such activities. This creates a constant risk of arrest, prosecution, and asset forfeiture. Regulatory frameworks often struggle to keep pace with the rapidly evolving technology used in dark markets, which exacerbates the challenges for law enforcement and regulatory agencies.
Furthermore, regulatory concerns extend beyond legal enforcement. As governments seek to combat money laundering, tax evasion, and the proliferation of illegal goods, they implement stricter regulations and oversight measures. These measures aim to disrupt the operations of dark markets but also pose significant operational hurdles for those involved. The risk of getting caught due to advanced monitoring tools and transaction tracing techniques continually looms, discouraging many from participating or investing in these underground platforms.

Overall, the risks and regulatory challenges associated with dark markets highlight the delicate balance between illicit innovation and enforcement efforts. Navigating this environment requires a keen awareness of legal boundaries and security threats, as well as an understanding of the ongoing efforts by authorities to regulate or shut down such platforms.
Market Manipulation and Abuse
Dark markets, often associated with illicit activities and anonymous transactions, pose significant risks and challenges to both users and regulators. These platforms facilitate a wide range of illegal transactions, including drug sales, counterfeit goods, and stolen data, making them a hotbed for criminal behavior. The anonymity provided by dark markets enables participants to operate with little fear of detection, which complicates law enforcement efforts to combat illegal activities.
Market manipulation and abuse are prevalent issues within dark markets. Traders and malicious actors often engage in tactics such as price fixing, pumping, dumping, and fake reviews to deceive other users or manipulate market conditions. Such practices undermine the integrity of these platforms, causing financial losses for unsuspecting participants and fueling illegal trade activities. The lack of regulation and oversight further exacerbates these issues, enabling continuous manipulation and abuse.
One of the primary risks associated with dark markets is the potential for scams and fraud. Users frequently encounter counterfeit goods, stolen data, or non-delivery of purchased items. Additionally, the unregulated nature of these platforms increases the likelihood of theft, hacking, and other cybercrimes that jeopardize user safety and financial security. The volatile and unpredictable environment of dark markets makes it difficult for users to trust the authenticity of transactions or claims made by other participants.
Legal and ethical challenges also arise with the existence of dark markets. Their operations often violate laws related to drug trafficking, intellectual property infringement, and money laundering. Authorities face hurdles in investigating and shutting down these markets due to their decentralized and encrypted nature. This ongoing threat requires coordinated efforts that focus on technological, legal, and policy-based solutions to mitigate risks and curb abuse.
Overall, dark markets present complex risks and challenges that threaten the safety, security, and integrity of online commerce. Combating these issues demands continuous advancements in cybersecurity, robust legal frameworks, and increased awareness among users about the dangers associated with participating in such clandestine environments.
Transparency and Data Limitations
Dark markets, often operating within the shadowy corners of the internet, pose significant risks and challenges for participants and law enforcement alike. These platforms facilitate exchanges of illicit goods and services, which inherently increase the likelihood of scams, fraud, and other criminal activities. Participants face the danger of losing money without recourse, as trust is difficult to establish in environments where transparency is minimal.
One of the primary challenges in dark markets is the inherent lack of transparency. Transactions are typically anonymized using encryption techniques and cryptocurrencies, making it difficult for authorities to track activities or identify malicious actors. This opacity hampers efforts to enforce legal regulations and disrupt illegal operations, allowing criminal networks to thrive with limited oversight.
- The lack of regulation leaves the dark web rife with offensive content and unsafe websites.
- Deep web websites have to be hosted somewhere, and Impreza Hosting is one of those anonymous dark web hosting services.
- But people can still access independent media via BBC Tor Mirror and similar dark web news portals.
- A VPN connection is key to gaining greater privacy, security, and freedom on and off the dark web.
- In the main text, we performed a longitudinal analysis of the time evolution of all COVID-19 specific listings and all listings mentioning COVID-19, as well as the PPE and medicines categories, as shown in Fig.
Data limitations further complicate efforts to combat illicit activities on dark markets. The limited availability and reliability of information make it difficult for researchers and law enforcement to gather intelligence or assess the scope of illegal trade. The clandestine nature of these marketplaces means that traditional surveillance and investigation methods are often ineffective, requiring advanced technology and international cooperation to make progress.
Overall, the risks and challenges associated with dark markets underscore the importance of ongoing efforts to improve detection, increase transparency, and develop effective strategies for disruption. As these marketplaces continue to evolve, staying ahead of technological and operational shifts remains crucial for maintaining the integrity of digital spaces and safeguarding lawful commerce.
Strategies for Navigating Dark Markets
Dark markets operate in the shadowy corners of the internet, often serving as hubs for illegal activities and illicit transactions. Navigating these environments requires a nuanced understanding of their unique dynamics, security measures, and the challenges involved. For individuals or entities interested in exploring or understanding darkmarkets, developing effective strategies is essential to ensure safety and confidentiality while minimizing risks. This article explores key approaches to successfully maneuver within these clandestine marketplaces, emphasizing the importance of anonymity, secure communication, and thorough research to avoid pitfalls.
Analyzing Market Indicators
Navigating dark markets requires a strategic approach to understand their complex and often hidden environment. Due to the clandestine nature of these markets, traders and participants must rely heavily on market indicators and analytical tools to make informed decisions. Developing a comprehensive understanding of the key signals and patterns can greatly enhance the ability to operate safely and effectively within this challenging landscape.

Analyzing market indicators is crucial for anyone involved in dark markets. These indicators include price trends, trading volumes, and transaction patterns, which can provide insights into market activity and potential opportunities or risks. Monitoring fluctuations and identifying anomalies can help traders anticipate changes, avoid scams, and optimize their transactions.
Furthermore, understanding the broader context of dark markets involves observing shifts in demand and supply, which are often reflected in price movements and trade frequency. Volume spikes can signal increased interest in specific assets, while sudden drops may indicate instability or manipulation. Keeping track of these indicators enables participants to adapt their strategies proactively.
It is also essential to employ analytical tools designed for dark market environments. These tools can help decrypt anonymized transaction data, detect suspicious activity, and assess the credibility of counterparties. By combining traditional market analysis with specialized software, users can navigate these opaque markets more confidently and reduce potential vulnerabilities.
Ultimately, successful navigation in dark markets relies on a disciplined approach to data analysis and a keen awareness of evolving indicators. Staying informed, vigilant, and adaptable will improve decision-making and increase the chances of successful and secure transactions within this controversial yet active segment of the global marketplace.
Timing and Execution Tactics
Navigating dark markets presents unique challenges that require a strategic approach to ensure safety, security, and successful transactions. These digital marketplaces operate outside conventional oversight, making it essential for participants to adopt careful timing and execution tactics. Proper planning can mitigate risks and increase the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes while maintaining anonymity and security.
One of the fundamental strategies is understanding the timing of operations. Participants should monitor market activity trends to identify optimal moments for entry or exit. This includes observing periods of high liquidity or activity to facilitate smoother transactions and avoid detection. Additionally, avoiding periods of heightened law enforcement focus or market shutdowns can reduce exposure to legal and security risks. Timing also involves patience—waiting for confirmation of reputation upgrades or successful trade completion increases confidence in the process.
Execution tactics are equally critical. Employing secure communication channels and encryption methods helps safeguard interactions. Diversifying methods for payment and withdrawal minimizes patterns that could be traced back to the user. Strengthening operational security involves regularly updating anonymity tools and avoiding the reuse of identifiers. When engaging with dark markets, prioritizing stealth and discretion during transactions is vital. Additionally, conducting thorough due diligence on vendors or buyers before proceeding reduces the likelihood of scams or disputes.

- Research market trends and activity cycles to identify the most opportune moments for transactions.
- Maintain up-to-date security measures, including encryption and anonymous payment methods.
- Limit communication details and verify counterparties before executing trades.
- Coordinate timing to avoid peaks in law enforcement activities or market disruptions.
- Implement a cautious and phased approach when engaging in significant transactions.
By carefully timing actions and executing trades with security-conscious tactics, participants can better navigate the complexities of dark markets. Success relies on balancing vigilance, discretion, and patience while continuously adapting to the evolving landscape to minimize risks and optimize outcomes.
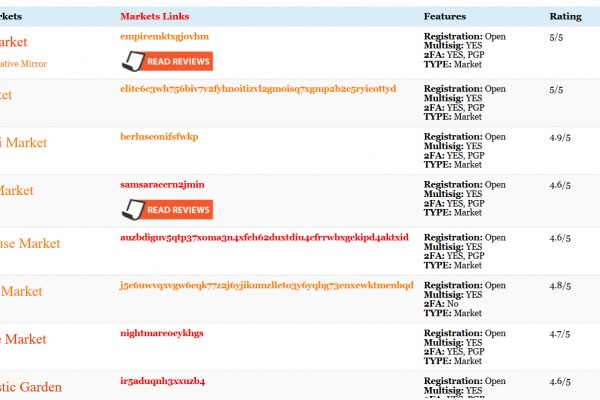
Risk Management Considerations
Dark markets, often associated with clandestine online trading platforms, pose unique challenges for participants due to their unregulated and anonymous nature. Navigating these environments requires careful strategic planning and robust risk management practices to mitigate potential legal, financial, and security threats. Understanding the landscape and implementing effective strategies are essential for those involved in darkmarkets to minimize vulnerabilities and protect their interests.
One fundamental strategy is thorough due diligence and information gathering before engaging in any transactions. This involves verifying the reputation of vendors or buyers, understanding the specific marketplace’s operational protocols, and assessing historical reviews or feedback. Being cautious about the sources and maintaining a low profile can help avoid scams or malicious activities commonly encountered in darkmarkets.
Risk management considerations should encompass a comprehensive approach to security, including the use of strong encryption methods for communications, employing secure payment channels, and regularly updating security protocols. It is crucial to limit the amount of sensitive information shared and to use anonymous or pseudonymous identifiers. Diversifying transaction risk by not relying heavily on a single marketplace or vendor can also reduce exposure to systemic failures or law enforcement actions.
Furthermore, establishing clear protocols for handling disputes, alongside methods for swift withdrawal or cessation of transactions, is important. Staying informed about law enforcement activities, technological developments, and emerging threats in the darkmarket space helps participants adapt their strategies effectively. Overall, a combination of cautious navigation and meticulous risk management can enhance safety and operational success in darkmarkets.


