Overview of Dark Markets
The dark market refers to a segment of the internet that operates outside the boundaries of conventional online platforms, often characterized by anonymous transactions and encrypted communications. These marketplaces are typically accessed via specialized browsers and enable users to buy and sell a variety of goods and services that are usually illegal or heavily regulated. The dark market plays a significant role in the broader landscape of cybercrime and illicit trade, attracting both criminals and those seeking untraceable transactions. Exploring the functionalities and risks of dark markets can provide valuable insights into the shadowy side of the internet and the importance of cybersecurity. For more in-depth information, visit a dedicated resource on dark market.
Definition and Characteristics
The term “dark market” refers to a segment of the internet that operates beyond the reach of traditional law enforcement and regulatory agencies. It is characterized by anonymous transactions and hidden networks, making it difficult to monitor and regulate activities taking place within these markets. These platforms are primarily accessed through specialized software that ensures user anonymity, such as the Tor network, allowing users to conceal their identities and locations.
Dark markets are typically known for facilitating the trade of a wide range of goods and services, some of which may be illegal or illicit. Common items exchanged include counterfeit currencies, firearms, illicit drugs, stolen data, and hacking tools. The anonymity and encryption features of these markets enable both buyers and sellers to operate with a higher degree of privacy compared to traditional online commerce platforms. This environment attracts individuals seeking to engage in activities that are prohibited or heavily regulated elsewhere.
Key characteristics of dark markets include decentralized operations, use of cryptocurrencies for transactions, and the reliance on secure and encrypted communication channels. These features help maintain the confidentiality of participants and protect them from detection. Despite their clandestine nature, dark markets often resemble legitimate e-commerce platforms, complete with reviews, seller ratings, and escrow services to facilitate trust among anonymous users. Understanding the structure and behavior of these markets is crucial for law enforcement and cybersecurity professionals aiming to combat illegal activities while balancing privacy rights and security concerns.
Evolution of Dark Market Platforms
The dark market refers to a segment of the internet where illicit goods and services are bought and sold outside traditional regulatory frameworks. Operating within the deep web, these markets facilitate transactions that often involve illegal items such as drugs, weapons, counterfeit currency, and stolen data. The anonymity provided by technical measures and the use of cryptocurrencies has contributed to the growth and accessibility of such platforms.
The evolution of dark market platforms has been marked by continuous innovation and adaptation to law enforcement efforts. Initially, these markets emerged as simple encrypted forums or chat rooms, but over time they have developed into sophisticated, resilient marketplaces. Some key stages in their evolution include:
- Early Platforms: These were often small, decentralized forums where users could trade illicit goods, but they lacked stability and reliable security measures.
- The Rise of Marketplaces: The advent of dedicated marketplaces, often modeled after legitimate e-commerce sites, enabled larger-scale trading with better user interfaces and escrow services for safer transactions.
- Use of Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: The integration of digital currencies like Bitcoin improved transaction privacy and reduced traceability, fueling growth in dark market activity.
- Law Enforcement Challenges and Market Shutdowns: Authorities have targeted prominent platforms, leading to their shutdown and the emergence of new markets that adapt quickly to avoid detection.
- Decentralized and Peer-to-Peer Networks: Recent developments include decentralized platforms that operate without a central server, making them more resilient to takedown efforts.
Overall, the dark market landscape continues to evolve as technology advances and law enforcement strategies adapt. Its persistence underscores the ongoing challenges in regulating and monitoring illicit online trade, making it a significant area of concern for cybersecurity and legal authorities worldwide.
Technology and Infrastructure Used
The underground world of the dark market represents a concealed segment of the internet where illegal goods and services are bought and sold beyond the reach of traditional law enforcement. These markets operate on hidden layers of the internet, often utilizing sophisticated technology to maintain anonymity and security for both buyers and sellers. Understanding the technology and infrastructure underpinning these platforms provides insight into their resilience and the challenges they pose to regulatory authorities.
Dark markets primarily rely on encrypted communication channels and decentralized networks to facilitate transactions while protecting user identities. Technologies such as Tor (The Onion Router) are central to their operation, enabling users to access these markets anonymously by routing traffic through multiple servers worldwide. This layered encryption makes tracking activities extremely difficult for outsiders, including law enforcement agencies.
In addition to Tor, many dark markets utilize cryptocurrencies as their primary mode of payment. Digital currencies like Bitcoin and Monero are preferred due to their pseudonymous or anonymous features, which help conceal transaction details and user identities. Smart contract protocols and decentralized exchanges further enhance privacy and reduce the risk of detection or interference.
The infrastructure supporting dark markets often includes secure hosting environments, encrypted messaging services, and sophisticated security measures to prevent hacking and infiltration. These platforms typically employ multi-layered security protocols, such as two-factor authentication and cold storage for digital assets, to minimize vulnerabilities. Constant updates and adaptations to emerging security threats are characteristic of the technology infrastructure in these markets, enabling them to operate effectively despite legal and technological pressures.
Overall, the technology and infrastructure used in dark markets are designed to maximize anonymity and security. While these features enable illicit activities, they also demonstrate the significant advancements in digital privacy and decentralized systems that are shaping broader cybersecurity and anonymity tools used across various sectors.
Product Offerings in Dark Markets
The dark market is a complex and often clandestine sector within the broader digital economy, primarily characterized by anonymous and unregulated transactions. Product offerings in this realm range from illicit goods and stolen data to counterfeit documents and unlicensed services. These markets operate outside the scope of traditional commerce, often leveraging cryptographic tools and encrypted networks to maintain privacy and security for both buyers and sellers. A significant aspect of dark markets is their diversity in products, making them a hub for a wide array of illicit activities. For those interested in understanding more about the structure and operations of these markets, exploring related dark market platforms can offer valuable insights.
Illegal Digital Goods and Data
The dark market serves as an clandestine environment where illegal digital goods and data are bought and sold outside the reach of traditional regulation. These markets operate primarily on encrypted networks, providing anonymity for both vendors and buyers involved in transactions that often include illicit software, stolen information, and other unauthorized digital products. The nature of these platforms poses significant challenges for law enforcement and cybersecurity professionals aiming to combat cybercrime and protect consumers from fraudulent activities.
In these dark markets, a variety of illegal digital offerings are available, including hacking tools, malware, counterfeit credentials, and sensitive personal or financial data. Such data can be exploited for identity theft, financial fraud, or cyber espionage. The anonymity afforded by these platforms makes it difficult to trace the origin of the goods and identify participants, thus fueling the persistence of these illicit activities. The proliferation of illegal digital goods in dark markets underscores the importance of robust cybersecurity measures and ongoing law enforcement efforts to disrupt these networks.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so does the sophistication of dark markets and the operations within them. The trade of illegal digital data not only harms individuals and organizations but also undermines trust in the digital economy. Stakeholders including businesses, government agencies, and cybersecurity experts must remain vigilant and proactive in detecting and mitigating threats originating from these illicit online environments. Safeguarding digital information and preventing illegal transactions in dark markets are crucial steps toward maintaining a safer digital ecosystem for all users.
Malicious Software and Cybercrime Tools
The dark market serves as a clandestine hub where a wide array of illicit products and services are exchanged, often operating beyond the reach of law enforcement and regulatory oversight. Among the most prevalent offerings are malicious software and cybercrime tools designed to facilitate illegal activities such as data breaches, identity theft, and financial fraud. These product offerings are tailored to meet the needs of cybercriminals, ranging from ransomware and remote access Trojans to phishing kits and exploit kits that exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems. The availability of such software on the dark market significantly contributes to the proliferation of cyber threats worldwide.
Dark markets provide a platform for vendors to sell malicious software and cybercrime tools with relative anonymity, often using encrypted communication methods. The offerings are frequently categorized by functionality, quality, and price, allowing buyers to select tools that best suit their operational needs. Malicious software sold in these markets may include turnkey kits that enable even novice cybercriminals to launch attacks, as well as sophisticated malware tailored for targeted campaigns. These product offerings are often sold with customer support, updates, and customization options, making them accessible to a broad spectrum of threat actors.
Throughout the evolution of dark markets, the trade in malicious software and cybercrime tools has become a significant component of cybercrime economies. The ease of access to such products lowers the barrier to entry for individuals seeking to engage in illegal activities, thereby fueling a rise in cyberattacks and data breaches. Security professionals emphasize that understanding the product offerings within these clandestine economies is crucial for developing effective defense strategies and disrupting the supply chain of malicious software. As these markets continue to evolve, efforts to monitor and dismantle them remain vital in combating cybercrime globally.

Stolen Payment Card Data and Accounts
The dark market represents a hidden segment of the internet where illegal goods and services are bought and sold outside the reach of conventional regulations. Among the most prevalent offerings in these clandestine marketplaces are stolen payment card data and compromised accounts. These products pose significant risks to individuals and businesses, fueling cybercrime activities and financial fraud.
Stolen payment card data is a primary commodity traded within dark markets, enabling cybercriminals to execute unauthorized transactions, drain bank accounts, and commit identity theft. The availability of such data often results from data breaches, phishing attacks, or malware infections. Buyers range from small-scale fraudsters to organized crime groups seeking to monetize stolen information rapidly. The sale of these payment details is facilitated through anonymized channels that protect the identities of both sellers and buyers, making enforcement challenging.
Alongside card data, **dark markets** also feature a wide array of compromised accounts, including email, social media, and financial platforms. These accounts are frequently acquired through hacking or phishing campaigns and are sold to facilitate further criminal activities like spamming, impersonation, or fraud schemes. Such access enables bad actors to exploit the accounts for financial gain or to launch targeted attacks against individuals or organizations.
The ecosystem of the dark market continuously evolves to adapt to law enforcement efforts and technological changes. Sellers often offer a range of products and services, including stolen credentials, hacking tools, and malware, creating a comprehensive environment for cybercriminal operations. Protecting oneself from these threats entails strong security measures, vigilant monitoring of financial transactions, and awareness of common tactics employed by offenders in these illicit markets.
Illicit Substances and Others
The dark market is a complex and often hidden segment of the internet where various illicit activities take place, including the offering of illegal products and services. Among the most common product offerings are illicit substances such as drugs, which are often sourced, sold, and distributed through anonymous online platforms. These markets enable buyers to purchase substances that are otherwise difficult to access through legal channels, often using cryptocurrencies to facilitate transactions securely and privately.
In addition to illicit drugs, dark markets frequently feature a range of other illegal products and services. These can include counterfeit documents, stolen data, hacking tools, and weapons. Vendors operating within these markets typically rely on encrypted communication methods and anonymizing technologies to avoid detection by law enforcement agencies. The variety of offerings in the dark market highlights its role as a hub for illegal trade and unauthorized goods.
It is important to understand that the presence of diverse product offerings in dark markets poses significant challenges to law enforcement and regulatory bodies. Efforts to combat such activities require a combination of technological sophistication, international cooperation, and legal frameworks to detect, dismantle, and prevent the proliferation of these illicit markets. Awareness and vigilance are essential for discouraging participation and mitigating the impact of illegal trade conducted within these hidden online spaces.
Market Dynamics and Business Models
Market dynamics and business models are fundamental concepts that shape the way industries operate and evolve. Understanding these elements is particularly crucial when examining less transparent sectors such as the dark market, where traditional economic principles often diverge from mainstream practices. The dark market operates within a complex environment influenced by clandestine activities, technological innovations, and shifting legal landscapes. It relies heavily on unique business models, driven by anonymity and decentralization, which challenge conventional regulatory frameworks. Analyzing these dynamics offers insights into how clandestine markets sustain themselves and adapt in response to law enforcement efforts and technological advancements. For those interested in exploring further, there are numerous resources available that delve into the intricacies of the dark market and its operational structures, including specialized marketplaces accessible through secure channels.
Marketplace Features and User Experience
- Illegal site templates may be the main reason for theft from Coinbase accounts, revealing the far-reaching effects of dark markets for the world of crypto.
- Fraudsters have been caught setting up complex scams involving stolen Paypal and eBay accounts that they use to buy high-value items.
- In my opinion, this normalized approach to cybercrime qualifies as “next generation” because it has transformed an obscure, niche activity into an accessible business model.
- The shutdown of Nemesis Market is expected to yield valuable data for further investigations targeting both sellers and users involved in criminal activities.
- Creating a new account on Incognito Market presents one with an ad for 5 grams of heroin selling for $450.
The landscape of digital commerce has expanded significantly, leading to diverse market dynamics and innovative business models that adapt to different user needs and regulatory environments. In particular, dark markets operate under unique conditions, often characterized by a lack of transparency and heightened security measures. These platforms rely on specific business models that emphasize anonymity and low transaction costs, frequently utilizing cryptocurrencies to facilitate seamless and private exchanges. Understanding these market dynamics is essential for grasping how dark markets function within the broader digital economy.
Marketplace features in these environments tend to prioritize privacy, security, and decentralization, often employing technology such as encryption, peer-to-peer networking, and anonymizing tools to protect users. User experience in dark markets can be complex due to the emphasis on confidentiality, requiring users to familiarize themselves with specialized tools and protocols to navigate safely. Despite these challenges, these features serve to attract individuals seeking secure avenues for exchange outside traditional financial systems, shaping the overall ecosystem’s resilience and adaptability.
In terms of business models, dark markets often operate on decentralized or semi-decentralized frameworks, relying heavily on reputation systems and escrow services to ensure trust among participants. The reliance on cryptocurrencies further differentiates these platforms from conventional marketplaces, offering both advantages and risks associated with digital currencies. As these ecosystems continue to evolve, understanding their market dynamics, innovative features, and the crucial importance of a user-centered approach remains vital for analysts, regulators, and users alike.
Ratings, Reviews, and Trust Mechanisms
The dark market operates within the hidden layers of the internet, often beyond the reach of traditional regulatory frameworks. Understanding its market dynamics and the business models employed is essential to grasp how these illicit platforms function and sustain their operations. Central to this environment are ratings, reviews, and trust mechanisms that, despite being unofficial, play a significant role in shaping user behavior and transaction safety.
Market dynamics in dark markets are predominantly driven by supply and demand for illegal goods and services. These platforms often facilitate anonymous transactions, relying heavily on encryption and cryptocurrencies to maintain privacy. The revenue streams are primarily derived from transaction fees, membership subscriptions, and commissions on sales. Business models tend to be decentralized, with multiple vendors operating independently within the marketplace, reducing the risk of total shutdown if one vendor is compromised.
Ratings and reviews are crucial components in maintaining a semblance of trust among users. Since formal legal protections are absent, the reputation system becomes the primary indicator of a vendor’s reliability. High ratings and positive reviews encourage more transactions, while negative feedback can deter buyers. These mechanisms are often manipulated or fabricated, which poses a challenge to genuine trustworthiness. Nonetheless, active feedback systems help buyers make informed decisions.
Trust mechanisms in dark markets include encrypted communication channels, escrow services, and vendor verification processes. Escrow services hold payments until buyers confirm receipt and satisfaction with the product. Vendor trust is bolstered through accumulated ratings and verified histories, which serve as informal qualifications. Despite the inherent risks, these trust mechanisms enable the dark market to function as a semi-organized ecosystem, where users rely heavily on reputation scores and feedback to mitigate potential scams.
In summary, the combination of complex market dynamics, innovative business models, and trust mechanisms allows dark markets to operate despite their illicit nature. Understanding these factors is essential for developing effective strategies to combat illegal online activities and to enhance cybersecurity awareness.
Payment and Escrow Systems
The landscape of modern commerce has evolved significantly, with various market structures shaping how goods and services are exchanged. In particular, the dark market operates within a complex framework of market dynamics and unique business models, often characterized by discreet transaction methods and alternative payment systems. Understanding these elements is crucial to grasping the functioning of this shadowy segment of the economy.
Market dynamics in the dark market are influenced by factors such as demand for illicit or hard-to-obtain products, anonymity concerns, and the need for secure transactional systems. Unlike traditional markets, where transparency and regulation play pivotal roles, dark markets rely heavily on inherent trust agreements and technological safeguards. These markets often experience rapid shifts in supply and demand, driven by law enforcement actions, technical innovations, and changing consumer preferences.
Business models within dark markets frequently emphasize decentralization and anonymity to protect participants. Many operate through peer-to-peer networks and utilize encrypted communication channels. Merchant and buyer relationships tend to be based on reputation systems, where trust is established through feedback scores and secure escrow mechanisms. Payments are often processed via digital currencies or other anonymous payment systems, providing a layer of security and privacy that conventional banking channels cannot offer.
Payment and escrow systems are fundamental to maintaining security and trust in dark markets. Escrow services serve as neutral third parties that hold funds until all parties fulfill their contractual obligations, minimizing the risk of fraud. Digital currencies like cryptocurrencies provide a practical solution for transactions by offering pseudonymity and ease of transfer across borders. These systems are designed to ensure that neither buyer nor seller is exposed to undue risk, fostering a transactional environment that, despite its illegitimate nature, operates on principles similar to legal marketplaces.
In the context of the dark market, these market dynamics and payment systems create a resilient infrastructure capable of sustaining illicit trade in the face of legal pressures and technical challenges. Understanding these elements is essential for comprehending how such markets manage to function continuously despite ongoing efforts to dismantle them. Ultimately, the interplay of innovative business models, advanced payment systems, and strategic market adaptations sustains the ongoing activity in these covert spheres of commerce.
Advertising and Promotion Strategies
The dark market represents a complex and often clandestine segment of the global economy, where traditional market dynamics and business models are significantly altered by the nature of anonymity and limited regulation. Operating primarily in encrypted and hidden networks, these markets thrive on unique advertising and promotion strategies that differ greatly from mainstream practices. Understanding these elements is essential for grasping how dark markets function and how they attract and retain illicit users.
Market dynamics within the dark market are characterized by high volatility, rapid shifts in demand, and a significant reliance on trust mechanisms due to the lack of formal regulation. Buyers and sellers often depend on reputation systems, escrow services, and peer reviews to establish credibility. The supply chain tends to be decentralized, with small-scale vendors offering specialized goods that are difficult to find through traditional channels. Fluctuations in law enforcement activity and technological advancements also heavily influence the stability and growth of these markets.
Business models in the dark market are adapted to facilitate anonymous transactions and bypass legal restrictions. Common models include commission-based sales, subscription services, and tiered access for vendors and buyers. Many vendors operate on a peer-to-peer basis, leveraging encrypted communication channels and cryptocurrencies to maintain anonymity. The focus is on minimizing traceability while maximizing transaction security, often through decentralized platforms or private networks. This creates an environment where illicit goods and services can be bought and sold covertly, reinforcing the resilience of the dark market ecosystem.
Advertising and promotion strategies in the dark market are discreet and often rely on word-of-mouth, forums, and reputation systems rather than public advertising. Vendors frequently promote their offerings through encrypted messaging apps and specialized online communities that cater to target audiences. Some use coded language and indirect references to evade detection by law enforcement and automated monitoring tools. Promotions are also built around establishing trust, ensuring buyers feel confident in their transactions despite the illegitimate nature of the market. Effective use of reputation management and discreet communication channels enables vendors to sustain their operations and grow their customer base in this underground space.
Overall, the dark market operates under a set of unique market dynamics, innovative business models, and clandestine promotion strategies that enable it to persist despite legal and technological challenges. Understanding these aspects provides insights into how illicit trade continues to evolve and adapt in a digitally connected world.
Cybercrime Infrastructure and How It’s Sold
Cybercrime infrastructure has evolved into a complex and clandestine network that enables the sale and distribution of illegal digital tools and services. The dark market serves as a hidden marketplace where cybercriminals can buy and sell malicious software, stolen data, and hacking services. These platforms facilitate a thriving underground economy, making it easier for criminals to coordinate operations and monetize their illicit activities. Understanding how cybercrime infrastructure is sold and traded in these covert markets is essential for developing effective cybersecurity strategies to combat these threats.
Remote Access and Server Listings
Cybercrime infrastructure has become a sophisticated network that supports illegal activities on the dark market, enabling criminals to operate with relative ease and anonymity. These underground markets facilitate the sale and distribution of malicious tools, stolen data, and hacking services, attracting a wide range of cybercriminals worldwide. A crucial aspect of this infrastructure involves remote access tools and server listings, which serve as the backbone for many malicious operations.
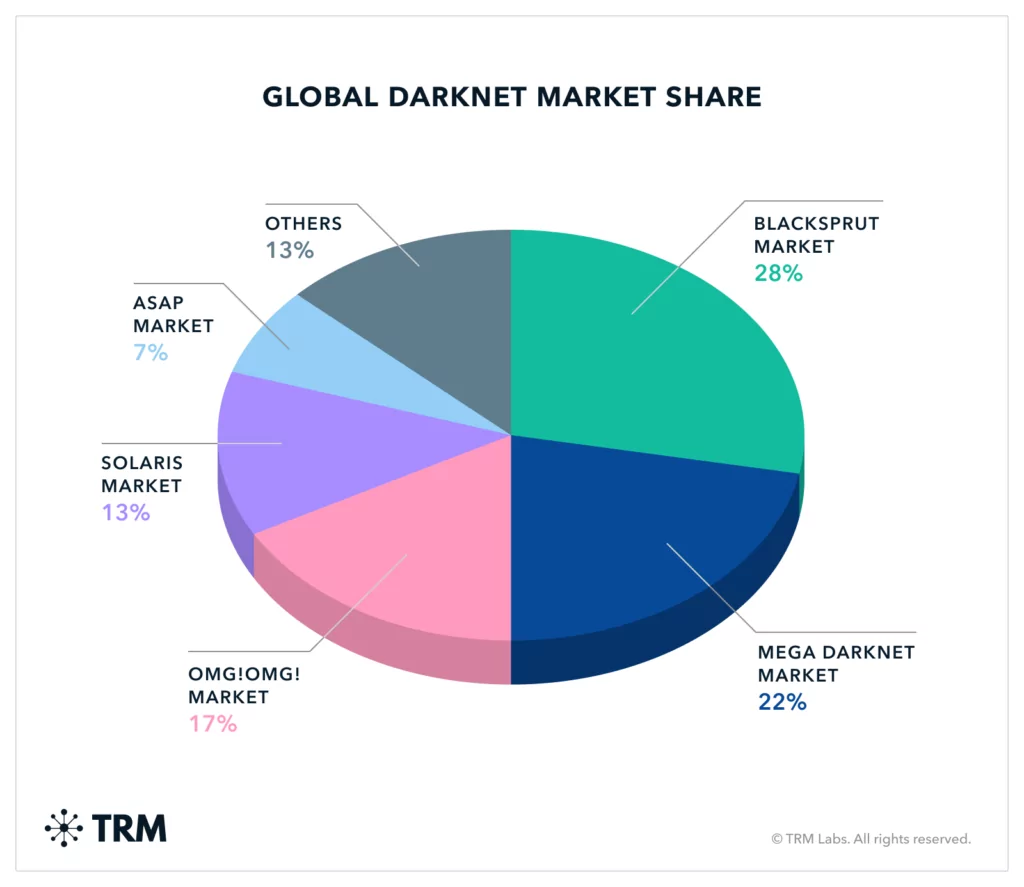
Dark markets often provide listings for compromised servers and remote access services that allow attackers to control infected machines remotely. These server listings include details about compromised servers, such as IP addresses, vulnerabilities, and access credentials, making it easier for cybercriminals to deploy malware or maintain persistent access within targeted networks. Such listings streamline the process of establishing footholds within victim environments, reducing the technical barriers for less experienced criminals.
Furthermore, the sale of remote access tools on the dark market enables cybercriminals to gain unauthorized entry into networks without needing to develop hacking techniques from scratch. These tools range from low-cost exploits to advanced remote desktop services, often sold as turnkey solutions. Buyers can instantly gain control over compromised systems, exfiltrate data, or launch wider attacks using these remote access capabilities.
Overall, the dark market’s role in distributing cybercrime infrastructure—including server listings, remote access tools, and hacking services—significantly contributes to the scale and sophistication of cyber threats. This underground ecosystem continuously evolves to bypass security measures, making it a persistent challenge for cybersecurity professionals aiming to combat cybercrime.
Use Cases for Stolen Infrastructure

Cybercrime infrastructure refers to the range of tools, services, and networks that cybercriminals establish and utilize to carry out malicious activities. These infrastructures often include phishing kits, malware delivery systems, command and control servers, cryptocurrency laundering services, and exploit kits designed to breach security defenses. The dark market serves as a crucial marketplace where such infrastructure is bought, sold, and traded, enabling cybercriminals to access sophisticated resources without the need to develop them from scratch. This underground economy facilitates the rapid deployment of cyberattacks and increases the scale and complexity of cyber threats across various sectors.
One common use case for stolen cybercrime infrastructure involves launching large-scale phishing campaigns. Cybercriminals purchase access to compromised email servers or exploit kits that can generate convincing fake websites or messages to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information. Similarly, malicious actors often acquire command and control servers through the dark market to manage botnets—networks of infected devices used for Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, spam campaigns, or data theft. These stolen infrastructures enable attackers to coordinate their operations more effectively and anonymously, complicating efforts to track and dismantle criminal networks.
Another expanding use case is the monetization of stolen credentials and personal data. Cybercriminals leverage the dark market to buy and sell databases containing usernames, passwords, financial information, and other sensitive data. This stolen data can then be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or selling on secondary markets for profit. In addition, cybercriminals often use preconfigured exploit kits sourced from the dark market to target vulnerable systems, allowing them to deploy ransomware or other malware quickly and efficiently. Overall, the dark market has become a central hub for trading cybercrime infrastructure that fuels a broad spectrum of illicit activities, posing significant challenges for cybersecurity defenses globally.
Examples of Stolen Systems for Sale
Cybercrime infrastructure refers to the complex network of tools, services, and digital platforms used by malicious actors to carry out illegal activities online. These infrastructures are often sold or distributed through dark markets, anonymous online marketplaces that facilitate the exchange of illicit goods and services. On these platforms, cybercriminals can acquire malware, hacking tools, stolen data, and access to compromised systems with relative ease. The dark market ecosystem enables cybercriminals to scale their operations, often leading to significant financial and data losses for individuals and organizations alike.
One of the most concerning aspects of dark markets is the sale of stolen systems and data. Cybercriminals frequently trade in compromised accounts, servers, and entire networks, making it easier for others to launch further attacks or exploit these systems for profit. These stolen systems include a variety of targets, such as financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies, each providing lucrative opportunities for hackers.
- Examples of stolen systems for sale include:
- Credentials for access to corporate and personal email accounts
- Databases containing sensitive customer information
- Remote access tools (RATs) that allow control over infected devices
- Complete compromised servers or hosting environments ready to be exploited
- Pre-installed backdoors on hacked systems, providing persistent access to cybercriminals
Dark markets facilitate the buying and selling of these stolen systems through encrypted communication channels, ensuring the anonymity of participants. This illicit trade not only fuels ongoing cyberattacks but also supports the growth of a large underground economy where stolen digital assets can be quickly bought, sold, and resold. Awareness of how cybercrime infrastructure is sold and utilized highlights the importance of robust cybersecurity practices to defend against these evolving threats.
Law Enforcement and Legal Actions
Dark markets, also known as dark web marketplaces, are hidden online platforms where various goods and services are bought and sold outside the reach of traditional law enforcement and regulatory agencies. These anonymous spaces facilitate a wide range of transactions, often involving illegal items such as drugs, weapons, and stolen data. Law enforcement agencies worldwide continuously work to identify and disrupt these operations through legal actions and advanced investigative techniques. Understanding the complexities of dark markets is essential for developing effective strategies to combat illicit activities and uphold legal standards. For more insights, you can explore additional resources related to dark market activities and enforcement efforts.
Notable Operations and Their Impact
The dark market represents a hidden segment of the internet where illegal goods and services are exchanged, often operating beyond the reach of traditional law enforcement. These clandestine marketplaces facilitate transactions involving narcotics, weapons, stolen data, and counterfeit products, posing significant challenges to authorities worldwide. Law enforcement agencies have increasingly dedicated resources to dismantling these operations, utilizing advanced cyber investigative techniques, infiltration strategies, and international cooperation to target key players.
Numerous notable operations have made headlines for their impact on disrupting dark market activities. These operations often involve extensive digital forensics, undercover work, and international collaborations to trace transactions and identify moderators and vendors. Successful takedowns can temporarily cripple specific marketplaces, but the resilient nature of these platforms often leads to the emergence of new sites. The ongoing efforts of law enforcement aim to create a deterrent effect and diminish the profitability of illegal online markets.

The impact of these law enforcement actions extends beyond immediate closures. They help in dismantling entire networks, recovering stolen assets, and gathering intelligence that can lead to broader criminal investigations. However, the technological and operational evolution of dark markets, including the adoption of privacy-enhancing tools and cryptocurrencies, complicates enforcement endeavors. Despite these hurdles, persistent efforts continue to uphold legal standards and protect public safety from the threats posed by these covert online operations.
Challenges in Disrupting Dark Markets
Disrupting dark markets presents significant challenges for law enforcement agencies worldwide as these platforms operate in hidden digital environments designed to evade detection. The anonymity features and encrypted communication channels used by dark markets make traditional investigative techniques ineffective, requiring specialized strategies and advanced technological tools. Legal actions against these illicit marketplaces often involve complex coordination across multiple jurisdictions, complicating enforcement efforts and delaying prosecutions.
One of the primary obstacles faced by authorities is the constantly evolving nature of dark markets. Operators frequently change domain names, employ robust encryption, and utilize decentralized structures to stay ahead of law enforcement efforts. This adaptability hampers efforts to dismantle these platforms swiftly and effectively. Additionally, victims and witnesses may be hesitant to cooperate due to fear of retaliation or lack of trust in authorities, further hindering investigations.
Legal challenges also include balancing privacy rights with the need for surveillance and investigative actions. While authorities seek to deploy advanced hacking techniques or undercover operations, these measures must comply with legal standards and respect individual rights, creating a complex legal landscape. International cooperation is crucial, as dark markets often span multiple countries, but differing legal frameworks and priorities can slow down or obstruct joint actions.
Despite the formidable challenges, law enforcement continues to develop innovative approaches for disrupting dark markets. These include targeting the financial infrastructure used to process transactions, infiltrating forums and communication channels, and employing cyber forensic techniques to trace digital footprints. Ultimately, persistent legal and technological efforts are essential in combating these illicit networks and mitigating their impact on society.
Legal Penalties and Deterrence
The dark market, often operating in the shadows of the internet, presents significant challenges for law enforcement agencies worldwide. These digital marketplaces facilitate the exchange of illegal goods and services, ranging from illicit drugs to counterfeit items, making them a focal point for legal actions aimed at maintaining order and safety. Authorities employ a variety of investigative techniques, including digital forensics, undercover operations, and international cooperation, to identify and shut down these clandestine platforms.
Legal actions against dark markets typically involve coordinated efforts to arrest operators, seize servers, and dismantle networks. Prosecutors pursue charges such as conspiracy, money laundering, and drug trafficking, depending on the nature of the illegal activities. Court proceedings aim to establish accountability and serve as a deterrent to individuals contemplating involvement in these illegal operations. The complexity of the dark market’s structure often necessitates sophisticated legal strategies and cross-border collaboration.
Legal penalties for those involved in dark markets are generally severe, reflecting the gravity of their offenses. Convictions can result in lengthy prison sentences, substantial fines, and asset forfeiture. These penalties serve to dissuade potential offenders by highlighting the risks associated with participation in illegal online marketplaces. Moreover, law enforcement agencies emphasize deterrence by publicizing successful operations and legal actions, signaling the government’s commitment to combating cybercrime. Through persistent enforcement and strict penalties, authorities aim to reduce the prevalence of dark markets and protect the public from associated harms.
International Cooperation and Future Efforts
The dark market has become a significant challenge for law enforcement agencies worldwide, given its anonymous nature and the scale of illicit activities it facilitates. Efforts to combat these underground platforms involve a combination of legal actions and international collaboration to effectively dismantle illegal networks and prevent their operation. Cooperation between countries is essential, as many dark markets operate across borders, leveraging encryption and decentralized structures to evade detection.
Law enforcement agencies are employing advanced technological tools and strategies, including cyber forensics, data analytics, and infiltration techniques, to identify and apprehend those responsible for running dark markets. Legal actions often involve coordinated operations that seize assets, shut down servers, and prosecute individuals involved in illegal transactions such as drug trafficking, weapons sales, and illicit services. Strengthening legal frameworks and sharing intelligence across jurisdictions are vital components in these efforts.
International cooperation plays a crucial role in addressing the global reach of dark markets. Initiatives among law enforcement agencies, international organizations, and cybersecurity firms facilitate information sharing and joint operations that aim to disrupt these illegal ecosystems. Efforts are also underway to develop and implement regulations that enhance cybersecurity and reduce vulnerabilities exploited by dark market operators.
Looking to the future, continuous advancements in technology and the evolving tactics of those operating dark markets necessitate adaptive strategies. Increased investment in global intelligence-sharing platforms and the development of new analytical tools are expected to improve detection and dismantling efforts. Ultimately, a multifaceted approach combining legal measures, technological innovation, and international collaboration will be essential to curbing the growth and impact of dark markets in the coming years.
Risks and Security Implications
The dark market represents a complex and often clandestine sector of the internet where transactions occur beyond the reach of conventional law enforcement and regulatory frameworks. Engaging with this environment introduces significant risks and security implications, including exposure to scams, fraud, and legal consequences. Users must navigate an array of potential threats that can compromise their privacy, financial assets, and personal safety. Understanding these risks is essential for anyone considering involvement in the dark market, as it demands heightened vigilance and security measures to mitigate potential harms.
Threats Posed by Dark Market Activities
The dark market represents a hidden segment of the internet where illegal activities flourish and pose significant risks to individuals, businesses, and governments. Operating outside the boundaries of legal regulations, these marketplaces facilitate the exchange of illicit goods and services, including stolen data, firearms, drugs, and counterfeit products. The anonymity features that make the dark market accessible also contribute to its threat level, making it difficult for authorities to track and dismantle criminal operations effectively.
One of the primary security concerns associated with dark market activities is the proliferation of cyber threats such as data breaches, identity theft, and financial fraud. Cybercriminals often utilize these platforms to sell stolen personal and financial information, which can then be used for malicious purposes. Additionally, the dark market acts as a hub for renting or purchasing malware, ransomware tools, and hacking services that can compromise corporate or individual systems, leading to potential data loss and operational disruptions.
The illegal trade conducted within these markets also fosters a range of safety and security risks, including the distribution of illicit substances and dangerous weapons. These activities can contribute to increased violence, undermine public safety, and create complex legal challenges for law enforcement agencies. Furthermore, dark market infrastructures often promote encrypted communication channels and cryptocurrency payments, which complicate efforts to trace and combat criminal activities effectively.
To mitigate the risks posed by dark market activities, organizations and individuals must prioritize cybersecurity measures, such as robust encryption, regular security audits, and employee training on potential online threats. Staying vigilant to the signs of compromised digital assets and understanding the threat landscape can help prevent falling victim to these criminal enterprises. Ultimately, addressing the security implications of the dark market requires a collaborative effort across technological, legal, and policy domains to reduce the proliferation of illegal activities and protect societal well-being.
Impact on Individuals and Organizations
The dark market represents a hidden segment of the internet where illegal transactions and exchanges of illicit goods and services occur, often shielded from traditional law enforcement oversight. Engaging with these platforms poses significant risks and security implications for both individuals and organizations. The anonymous nature of the dark market makes it an attractive environment for cybercriminals, but it simultaneously exposes users to numerous vulnerabilities, including exposure to malicious actors, scams, and theft. These risks can result in financial losses, legal consequences, and damage to personal or corporate reputations.
For individuals, accessing the dark market can lead to severe security threats, such as identity theft, malware infections, or being targeted for extortion. Personal information or financial data obtained through illicit channels can be exploited for fraudulent activities, leading to long-lasting repercussions. On an organizational level, involvement with dark market activities can compromise sensitive corporate data, intellectual property, and customer information. This exposure not only undermines trust but can also lead to regulatory penalties and litigation.
The impact on security extends beyond individual compromises to broader organizational threats. Cybercriminals operating within the dark market often employ sophisticated tactics to infiltrate systems, such as ransomware attacks or data breaches. These incidents can disrupt essential operations, result in substantial financial costs, and tarnish brand integrity. Moreover, efforts to combat dark market activities require advanced cybersecurity measures and proactive monitoring, underscoring the importance of robust security protocols.
Overall, navigating the dark market entails considerable danger for both individuals and organizations. Awareness, strong security practices, and legal compliance are critical components to mitigate these risks. Recognizing the dangers associated with this clandestine environment is essential in safeguarding digital assets and maintaining secure online interactions.
Strategies for Prevention and Defense
The dark market presents significant risks and security challenges for individuals and organizations engaging with or operating within this environment. These marketplaces are often associated with illicit activities, making them a prime target for cybercriminals and law enforcement agencies alike. Understanding these risks and implementing effective strategies for prevention and defense are essential to mitigate potential threats.
Risks associated with the dark market include exposure to illegal transactions, financial loss, identity theft, and legal repercussions. Participants may unknowingly become involved in criminal schemes, which can lead to prosecution or damage to reputation. Additionally, websites operating within the dark market are frequent targets for hacking attempts, malware distribution, and data breaches, increasing the threat landscape significantly.
To safeguard against these risks, implementing robust security strategies is crucial. Some key strategies include:
- Employing strong encryption protocols to secure communication channels, preventing interception of sensitive data.
- Using multi-factor authentication to verify user identities and reduce unauthorized access.
- Conducting regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities within systems and networks.
- Maintaining updated software and security patches to defend against known exploits.
- Implementing monitoring tools to detect suspicious activities and potential breaches promptly.
- Providing comprehensive training for personnel on best security practices and recognizing phishing attempts.
- Establishing strict access controls to limit exposure of sensitive information only to authorized individuals.
Given the clandestine nature of the dark market, organizations and individuals should prioritize proactive measures to prevent breaches and maintain operational security. Combining technical defenses with user awareness significantly enhances resilience against evolving cyber threats in this environment. Recognizing that the risk landscape is continually changing, ongoing vigilance and adaptation are essential for effective security management in the dark market space.
Ethical and Societal Considerations
The dark market presents a complex landscape at the intersection of technology, ethics, and society. As online platforms facilitate the exchange of goods and services outside traditional regulatory frameworks, significant ethical considerations arise regarding legality, safety, and morality. The unchecked nature of these marketplaces often raises concerns about criminal activities, impacts on public health, and the potential for exploitation. Understanding the ethical and societal implications of attending or engaging with a dark market is crucial for fostering informed discussions and promoting responsible behavior in digital spaces.
Normalization of Cybercrime Business Models
The emergence of the dark market has raised significant ethical and societal concerns, primarily due to its role in facilitating illegal activities and undermining the rule of law. These clandestine platforms provide a space where illicit goods and services, including weapons, drugs, and stolen data, are bought and sold with relative anonymity. This normalization of cybercrime business models within the dark market ecosystem poses serious risks to societal safety, economic stability, and individual privacy. As these platforms become more sophisticated, they further blur the lines between lawful commerce and illicit enterprises, challenging authorities and ethical standards alike.
One of the main societal challenges associated with the dark market is its contribution to the normalization of cybercrime as a viable business model. This commodification incentivizes criminal behavior by offering a seemingly organized and lucrative framework for illegal activities, which can attract new participants and perpetuate cycles of crime. The ease of access and perceived legitimacy of these digital marketplaces can lead to increased criminal ventures, complicating efforts for law enforcement agencies to combat cybercrime effectively. Additionally, the proliferation of these markets can erode public trust in digital infrastructure and online transactions, undermining societal confidence in technological advancements.
Ethically, the existence and operation of the dark market pose questions about responsibility and morality in both the digital and physical worlds. While many argue that these platforms exploit vulnerabilities within the internet’s architecture, others believe that technological innovation should be accompanied by improved regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines. Society must consider how to balance technological progress with moral obligations to prevent the misuse of online spaces for harmful purposes. Addressing these issues requires a collaborative effort between governments, technology providers, and civil society to develop strategies that disrupt these illegal networks while respecting individual rights and freedoms.
In conclusion, the dark market exemplifies the complex intersection of technology, ethics, and society. Its facilitation of cybercrime business models underscores the urgent need for comprehensive measures to prevent exploitation and uphold societal values. Ensuring online security, fostering ethical standards for digital commerce, and strengthening legal frameworks are essential steps toward mitigating the adverse impacts of such illicit platforms and promoting a safer digital environment.
Challenges in Public Awareness
The dark market presents significant challenges from ethical and societal perspectives, raising concerns about legality, safety, and moral responsibility. These illicit online marketplaces facilitate the exchange of illegal goods and services, often evading regulatory oversight and legal enforcement, which complicates efforts to promote public awareness and understanding. The secrecy inherent in dark markets makes it difficult for consumers and authorities to ascertain the risks involved, thereby increasing the likelihood of harm and criminal activity.
One of the primary societal challenges is the difficulty in educating the public about the dangers associated with engaging in activities on the dark market. Many users may not fully comprehend the legal implications or the potential consequences of purchasing or selling illegal items. This gap in awareness can lead to increased victimization, participation in criminal operations, and support for illicit markets, perpetuating cycles of violence and corruption.
Ethically, there is an ongoing debate about the responsibilities of law enforcement, technology companies, and society in tackling the issues posed by dark markets. While efforts to monitor and shut down these platforms are essential, there is also a need to balance security measures with protecting individual privacy rights. Addressing the societal challenges requires transparent communication, public education campaigns, and collaborative strategies that highlight the importance of lawful behavior and the dangers associated with illicit online environments.
Overall, overcoming the challenges in raising public awareness about the dark market involves educating users about the risks and legal consequences while fostering a societal understanding of the broader impact that these illicit activities have on communities and institutions. Only through informed awareness and ethical responsibility can meaningful progress be made in mitigating the influence of dark markets and promoting safer, lawful online interactions.
Need for Improved Cybersecurity Practices
The existence of dark markets has become a significant concern in the realm of cybersecurity and societal safety. These hidden online platforms facilitate the exchange of illicit goods and services, often enabling criminal activities such as drug trafficking, weapon sales, and data breaches. The anonymity provided by these markets complicates law enforcement efforts and raises profound ethical questions about privacy, security, and the impact on society as a whole. Addressing these issues requires a careful balance between respecting individual privacy rights and ensuring public safety.
As the prominence of dark markets grows, it underscores the urgent need for improved cybersecurity practices across both public and private sectors. Enhanced security measures can help prevent unauthorized access, data theft, and the proliferation of illegal activities associated with these platforms. Organizations must adopt advanced encryption, regular security audits, and comprehensive threat detection systems to mitigate vulnerabilities and protect sensitive information.
Furthermore, with the increasing sophistication of cybercriminals operating within dark markets, there is a moral obligation to develop collaborative strategies for cybersecurity. This includes sharing intelligence, implementing strict regulations, and fostering international cooperation to dismantle these illegal networks. Promoting ethical hacking and cybersecurity awareness can also contribute to a safer digital environment, discouraging malicious actors from exploiting vulnerabilities.
Ultimately, confronting the challenges posed by dark markets necessitates a multi-faceted approach that prioritizes ethical considerations while strengthening cybersecurity defenses. Building resilience against cyber threats not only protects individual privacy but also safeguards societal stability, ensuring that technological advancements serve the greater good rather than facilitating harm.