Overview of Dark Market URLs
The dark market is a hidden segment of the internet where illicit transactions and illegal goods are often exchanged. These markets operate on encrypted networks, making them difficult to monitor and shut down. One notable aspect of dark markets is the use of specialized URLs, known as dark market URLs, which serve as gateways to these clandestine marketplaces. These URLs are often obfuscated and frequently change to avoid detection. For example, a well-known dark market URL might look like http://abacusborncrffug2ytuqx3fczqbou4mrev56pfliv7ipjfi4uib7cad.onion. Understanding how these URLs function is crucial for cybersecurity professionals and law enforcement agencies aiming to combat illegal activities online. Visiting and exploring dark market URLs can lead to encounters with various risks, emphasizing the importance of caution and awareness when discussing or studying these platforms.
Definition and Role of Dark Market URLs
Dark market URLs are web addresses that provide access to online marketplaces operating within the dark web, a part of the internet not indexed by standard search engines and accessible only through specialized anonymizing software. These URLs serve as gateways for users to browse and purchase illicit goods and services, often leveraging encryption and anonymity protocols to protect both sellers and buyers. Understanding the role of dark market URLs is crucial for cybersecurity professionals, law enforcement agencies, and researchers analyzing underground digital activities.
Dark market URLs play a pivotal role in facilitating illegal transactions by acting as centralized hubs within the dark web ecosystem. They enable vendors to list illicit products such as weapons, drugs, stolen data, and counterfeit documents, while buyers can access these offerings privately and securely. These URLs often change frequently to evade detection and shutdown by authorities, making it challenging for law enforcement to track and dismantle the markets effectively.
- Identification and Access: Dark market URLs are unique and often complex, requiring users to know the exact address or access through hidden service directories.
- Operational Function: They serve as platforms where vendors can showcase their offerings, and buyers can browse and communicate securely.
- Security and Anonymity: Dark market URLs utilize encryption protocols and anonymity networks to conceal user identities and locations.
- Transient Nature: Due to enforcement actions, many dark market URLs are short-lived, with new addresses emerging regularly.
Recognizing these URLs and understanding their role within the dark web landscape is essential for developing effective strategies to combat organized illegal activities. The constant evolution of dark market URLs underscores the importance of ongoing cybersecurity efforts and legal cooperation to mitigate their impact.
Common Features of Dark Market Websites
Dark market URLs are web addresses used to access clandestine online marketplaces that operate outside the traditional internet network. These platforms are often associated with illegal activities such as drug trafficking, weapon sales, stolen data exchanges, and other illicit trades. Access to these sites typically requires specialized browsers or networks, such as the Tor network, which provides anonymity to both vendors and buyers. Understanding the structure and features of dark market websites is essential for cybersecurity professionals and law enforcement agencies aiming to monitor and counter illegal online activities.
Dark market URLs usually share common characteristics that distinguish them from regular websites. Many employ complex, frequently changing domain names or utilize onion addresses for enhanced privacy and security. These URLs often incorporate random or encoded strings that make them difficult to track or predict. The websites themselves often feature user interfaces resembling legitimate e-commerce platforms, complete with product categories, vendor ratings, and secure payment options. Security measures such as encrypted communications and anonymized transactions are standard features, ensuring the confidentiality of both parties involved.
Additionally, dark market websites prioritize user anonymity and security through various means. They often include escrow services to protect buyers and sellers, and adopt reputation systems to evaluate trustworthiness. Forums and communication channels are embedded within these sites for vendors and buyers to discuss, review, and verify identities. The combination of these features and the use of specific dark market URLs facilitate the seamless operation of illicit marketplaces in the shadows of the internet, making them a persistent challenge for authorities seeking to curb illegal online trade activities.
Access and Anonymity of Dark Market URLs
The accessibility and anonymity of dark market URLs play a crucial role in maintaining privacy and security for users seeking illicit goods and services online. These hidden marketplaces operate on encrypted networks, making it challenging to trace participants or locate the exact URLs. Accessing a dark market URL often requires specialized software or configurations to ensure anonymity, such as the Tor network, which masks users’ identities. The dark market url is typically changed frequently to avoid detection and shutdown by authorities. For those interested in exploring such hidden sites, understanding the importance of secure access is vital. Learn more about this topic and discover alternative marketplaces at this link to see how these platforms operate while maintaining user privacy.
Use of Tor and Other Anonymity Software
Accessing dark market URLs typically involves the use of specialized anonymity tools designed to protect users’ identities and locations. These platforms often operate on hidden services, making it challenging to trace participants or locate the actual physical sites. Users frequently turn to networks like Tor to browse these URLs securely and anonymously. Tor, which stands for The Onion Router, encrypts internet traffic and routes it through multiple volunteer-operated servers worldwide, effectively masking users’ IP addresses and online activities. This layered encryption provides a degree of anonymity that is crucial for accessing dark markets without revealing one’s identity.
Beyond Tor, there are other anonymity software options such as I2P and VPNs, which some users utilize to further obfuscate their digital footprints. While these tools can enhance privacy, they also introduce complexity and potential vulnerabilities if not properly configured. Accessing dark market URLs, such as the one at darkmarketwebsiteonion, requires careful consideration of security measures to avoid detection or compromise. Maintaining anonymity is vital for both users and operators of these markets, as law enforcement agencies employ various strategies to track activities on these hidden platforms.
Overall, the use of Tor and other anonymity tools is central to accessing dark market URLs securely. These technologies enable users to navigate hidden services while safeguarding their personal information from surveillance or legal repercussions. However, it is essential to recognize that while these tools can provide significant privacy benefits, they are not infallible, and users should stay informed about best practices for online anonymity and security.
Technical Aspects of Dark Market URL Architecture
Dark market URLs serve as essential gateways to clandestine online marketplaces where anonymity and secure access are paramount. These URLs typically utilize specialized domain extensions and protocols that obscure the location and identity of the hosting servers, making them difficult to trace and monitor. Access to dark market URLs often requires specific tools such as the Tor browser, which enables users to connect through encrypted, anonymized networks, ensuring that their activity remains private. This technical setup helps protect both buyers and sellers from detection by law enforcement agencies and other outsiders.
The architecture of dark market URLs is carefully crafted to enhance security and anonymity. These URLs frequently employ layered encryption and decentralized server distribution to prevent shutdowns and takedowns. They are often hosted on hidden services, which are accessible only through anonymous networks and do not expose the true IP addresses of the servers. Furthermore, the use of unique subdomains and frequently changing URLs complicates efforts to track or block these marketplaces, maintaining their operational resilience.
Understanding the technical aspects of dark market URL architecture sheds light on how these platforms maintain their secrecy and continued operation. By leveraging specialized network protocols, encryption, and dynamic URL strategies, dark markets can remain accessible to authorized users while evading detection. This complex infrastructure underscores the importance of sophisticated technical measures in supporting anonymous and secure transactions within these illicit online environments.
Types of Markets and Their URL Structures
Understanding the different types of markets and their URL structures is essential for navigating the online landscape effectively. Markets can generally be categorized into traditional, digital, and dark markets, each with distinct characteristics and ways of organizing their web presence. Dark markets, in particular, are often accessed through specialized URLs that mask their true nature and facilitate anonymous transactions. These URL structures typically involve complex, non-search engine friendly formats, making them harder to find unless specific links are known. For instance, some dark markets utilize onion addresses to ensure privacy and security. Exploring these hidden marketplaces requires awareness of their unique URL patterns and the necessary precautions when accessing them. For example, a dark market URL like http://xv3dbyu75coadsrwlbofnsg3dj5axfzcxh5v4nrvtcn3ey7uv6vrf5yd.onion exemplifies the complexity and anonymity designed into such sites. To learn more about dark markets and their structures, you can visit specialized resources that provide insights into these covert online spaces.
Drug Markets
Dark markets, also known as dark web marketplaces, operate within encrypted and anonymized networks, providing a platform for a variety of illicit goods and services. These markets often utilize distinct URL structures to maintain user anonymity and security. Typically, their URLs are not accessible through standard search engines and tend to use complex, alphanumeric domain names or specialized onion addresses that require specific software such as Tor Browser. The URL structures in dark markets are deliberately designed to obscure the true nature and location of the sites, making them difficult to trace and shut down.
Dark market URLs often follow specific patterns depending on the network they are hosted on. For example, many operate on onion sites with URLs ending in “.onion,” which are only accessible via the Tor network. These URLs may be randomly generated strings of characters, such as abc123xyz.onion, serving as a form of pseudonym to avoid detection. Other dark markets may utilize traditional domain extensions but incorporate layers of obfuscation within their URL structures to protect their identities and users. The use of such complex URL structures helps maintain the security and anonymity essential to dark markets.
Understanding the different types of markets and their URL structures is crucial for recognizing the online landscape of illicit commerce. The dark market URL structures exemplify how these platforms prioritize privacy and security. They often evolve rapidly, changing URLs to evade law enforcement efforts. This dynamic nature underscores the importance of cybersecurity awareness and vigilance when analyzing online activities related to dark web marketplaces. By monitoring the URL patterns and structures, authorities and cybersecurity professionals can better understand and combat illegal activities conducted across these clandestine platforms.
Stolen Data and Fraudulent Services
The dark market is a segment of the internet that operates outside the boundaries of standard online marketplaces, often involved in illicit activities such as buying and selling stolen data and fraudulent services. These markets typically consist of various types of platforms, each designed to facilitate specific transactions while maintaining anonymity for their users. Understanding the different types of markets and their URL structures is essential for recognizing potential threats and safeguarding digital assets. Dark market URLs often have hidden or obfuscated structures to evade detection and shutdown efforts, sometimes employing layers of encryption or unique domain naming conventions.
Dark markets can generally be classified into several categories based on their function and the type of data or services they offer. These include marketplaces for stolen data, counterfeit goods, drugs, weapons, and fraudulent services such as hacking tools or identity theft kits. The URL structures of dark markets frequently feature complex patterns, often changing domains or utilizing specialized hosting services to avoid takedown. For example, a dark market URL might resemble hiddenmarketxyz.com or use a subdomain with random characters to mitigate tracking efforts.
Stolen data, such as credit card information, login credentials, or personal identification details, is a common commodity sold within dark markets. These platforms facilitate the exchange of such sensitive information, often through secure or encrypted channels. Fraudulent services include hacking, phishing kits, and malware distribution, which are also frequently promoted within dark market environments. Recognizing the URL structures and patterns used by these sites, like unconventional domain extensions or dynamically generated addresses, can aid in identifying and monitoring potentially dangerous online spaces.
Staying aware of the characteristics of dark market URLs, such as the use of some suspicious or obscure naming conventions, can help cybersecurity professionals and internet users better defend against threats tied to stolen data and fraudulent services. Maintaining robust security practices and being cautious of unfamiliar or suspicious links is crucial in minimizing exposure to these clandestine online markets.
Illicit Goods and Services Marketplaces
Dark markets, often referred to as hidden marketplaces, operate on the deep web and facilitate the exchange of a variety of goods and services outside traditional regulatory frameworks. These marketplaces typically utilize specialized URL structures that help maintain user anonymity and secure transactions. Understanding the different types of markets and their URL configurations can provide insight into how these illicit platforms are organized and accessed.
In general, marketplaces are classified based on the types of goods and services they offer. Legal markets include retail, wholesale, and specialized niche markets, each with distinct URL structures designed for ease of access and navigation. Conversely, illicit markets, such as dark markets, are characterized by secretive URL schemes that often change frequently to avoid detection. These URLs frequently include unique identifiers or encrypted elements that obscure their true nature, making them challenging to locate or block.
Dark market URLs are intentionally designed to protect both vendors and buyers, often employing complex structures that hide their location and purpose. For example, such URLs may contain random alphanumeric strings, encrypted components, or specific patterns that distinguish them from standard websites. Regular updates or changes to these URLs are common to minimize the risk of shutdown by authorities or monitoring agencies. Dark market sites also often categorize their listings under various sections, with URLs reflecting these divisions to facilitate user navigation while maintaining anonymity.
Understanding the intricacies of dark market URL structures helps shed light on how these illicit platforms operate under the radar. While typical market URLs are straightforward and adhere to standard conventions, dark market URLs tend to be more complex and dynamic. This complexity is a strategic feature to evade detection and shutdown efforts. For instance, a dark market URL like https://darkmarketexample.com/abc123xyz might represent a specific marketplace or section within an illicit platform, emphasizing the use of non-descriptive paths and random segments.
Overall, the distinction between legitimate marketplace URL structures and those used by dark markets underscores the importance of cybersecurity awareness and the need for vigilant monitoring of online platforms. Recognizing the patterns and characteristics of dark market URLs can assist law enforcement and cybersecurity professionals in identifying and combating illegal online activities.
Detection and Monitoring of Dark Market URLs
Detecting and monitoring URLs associated with dark markets is crucial for maintaining online security and safeguarding sensitive information. These hidden marketplaces often operate outside the reach of traditional search engines, making their identification a challenging task. Effective detection involves analyzing various signals and behaviors that indicate the presence of dark market activity, such as specific URL patterns and hosting behaviors. Continuous monitoring helps track changes and new entries within these markets, allowing authorities and cybersecurity professionals to respond swiftly. For instance, monitoring sites like dark market URLs can provide valuable insights into illicit activities and emerging trends. Engaging with resources like dark market monitor can aid in staying vigilant against evolving threats in the shadowy corners of the internet.
Dark Web Monitoring Tools
Detection and monitoring of dark market URLs are critical components in cybersecurity strategies aimed at safeguarding organizations and individuals from illicit activities. Dark market URLs serve as access points to illegal marketplaces that host transactions involving stolen data, illicit goods, and other nefarious content. Identifying these URLs promptly can prevent data breaches, financial crimes, and support law enforcement initiatives. Utilizing sophisticated dark web monitoring tools enables security teams to track emerging threats, analyze patterns, and stay ahead of malicious actors operating within the underground economy.
Dark web monitoring tools employ a combination of automated crawling, data analysis, and real-time alerts to detect suspicious dark market URLs. These tools scan various underground forums, marketplaces, and hidden services, collecting intelligence on emerging criminal activities. By integrating threat intelligence feeds and machine learning algorithms, organizations can identify new dark market URLs as soon as they appear, facilitating swift responses. Continuous monitoring allows for early detection of potential threats, reducing damage and enabling proactive measures.
Effective detection also involves identifying the characteristics and behaviors associated with dark market URLs. These include patterns in domain registration, hosting providers, and activity timestamps. Security teams often leverage specialized software that can monitor dark web communications and surface relevant URLs that may pose risks. Staying updated with trends in the dark web allows analysts to anticipate and neutralize new threats before they escalate.
In conclusion, the detection and monitoring of dark market URLs are essential for maintaining cybersecurity resilience. Employing advanced dark web monitoring tools provides organizations with the insight needed to identify malicious sites, understand threat vectors, and take appropriate action. As the landscape of dark markets continues to evolve, ongoing vigilance and technological adaptation remain vital to protect digital assets and maintain safety in cyberspace.
Challenges in Tracking Dark Market URLs
The detection and monitoring of dark market URLs present significant challenges for authorities and cybersecurity professionals striving to combat illicit online activities. These clandestine marketplaces are often designed to operate discreetly, utilizing various encryption techniques and obfuscation methods to evade detection. Dark market URLs such as darkmarketexample.com are frequently disguised through the use of anonymized hosting services, making it difficult to trace their real locations and administrators. Additionally, these sites often change their URLs frequently or employ dynamic domain generation algorithms, complicating efforts to monitor or shut down their operations effectively.
Another major challenge in tracking dark market URLs is the use of encryption and privacy tools that obscure IP addresses and user identities. Criminals leverage VPNs, proxy servers, and Tor networks to hide their footprints, making it arduous for researchers and law enforcement to gather actionable intelligence. Moreover, these marketplaces typically operate within encrypted environments that prevent straightforward crawling or scraping, hindering automated detection processes. The frequent use of hidden communication channels and coded language also complicates keyword-based monitoring strategies, necessitating more sophisticated analysis techniques.
Furthermore, the decentralized and distributed nature of many dark markets means there is no central point of failure or single URL to target. When one dark market URL like darkmarketexample.com is taken down, new sites often emerge rapidly to fill the void, demonstrating the resilience of these networks. This constant evolution demands continuous and adaptive monitoring approaches, combining technical tools with intelligence gathering and community engagement. Overall, the complex and clandestine operational tactics of dark market sites pose ongoing hurdles for detection and tracking efforts aimed at disrupting illegal activities online.
Law Enforcement Actions Targeting Dark Market URLs
Law enforcement agencies worldwide are increasingly targeting dark market URLs to combat illegal activities conducted online. These clandestine marketplaces often facilitate the sale of illicit goods and services, making them prime targets for disruption and closure efforts. Efforts to dismantle these platforms focus on identifying key dark market URLs and taking strategic actions to shut them down, thereby reducing their impact on criminal networks. For instance, authorities have successfully attacked sites like http://xv3dbyu75coadsrwlbofnsg3dj5axfzcxh5v4nrvtcn3ey7uv6vrf5yd.onion, which is known for hosting a variety of illegal transactions. Continuous monitoring and enforcement are vital to disrupting the operations maintained through these dark market URLs and safeguarding digital spaces from exploitation.
Shutting Down Dark Market Sites
Dark markets have become a prominent part of the underground internet landscape, facilitating anonymous trade of illegal goods and services. Law enforcement agencies worldwide continuously work to disrupt these operations by targeting the specific URLs hosting dark market sites. These actions aim to dismantle illegal marketplaces, protect public safety, and disrupt criminal networks involved in activities such as drug trafficking, illicit arms sales, and stolen data exchanges.
Strategies used by authorities to shut down dark market URLs often involve coordinated efforts that include cyber operations, infiltration, and legal actions. These efforts typically focus on identifying the servers hosting the marketplaces and issuing takedown notices or arrest warrants for key operators. Once a dark market URL is seized or redirected, the entire platform’s operations are effectively halted, preventing continued illegal activity.
- Identification of the dark market URL through cyber investigations and intelligence gathering.
- Legal procedures to obtain warrants for server confiscation or takedown orders.
- Partnerships between government agencies and private sector cybersecurity firms to locate and disable illegal sites.
- Implementation of takedown operations to shut down the dark market URL and remove access for users.
- Monitoring and follow-up to prevent the creation of new sites by the same entities or individuals.
These enforcement actions serve as a critical tool in combating cyber-enabled crime. By targeting dark market URLs, authorities diminish the reach of illegal networks and send a clear message about the risks and consequences associated with operating or participating in such platforms. Continued effort and coordination are essential to stay ahead of evolving tactics used by criminals to evade law enforcement and maintain their dark market operations.
Case Studies of Dark Market URL Seizures
Dark markets, also known as dark web marketplaces, have become prominent hubs for illicit activities, including drug trafficking, arms sales, and other illegal transactions. Law enforcement agencies worldwide continuously monitor these platforms to identify and dismantle operations that exploit the anonymity of the dark web. A key aspect of these efforts involves targeting and seizing illegal dark market URLs, aiming to disrupt criminal networks and remove harmful content from the internet. These operations often require meticulous investigation, cooperation across jurisdictions, and advanced technical tools to trace illicit transactions back to their sources.
One notable case involved the seizure of a major dark market URL that was known for facilitating the trade of illegal substances. Authorities utilized a combination of undercover operations, cyber sleuthing, and legal procedures to track the operators and administrators behind the platform. The seizure of this URL not only shut down the marketplace but also served as a significant blow to the online illegal trade ecosystem. Such actions demonstrate the importance of proactive enforcement to combat the proliferation of dark web marketplaces.
Another example includes the dismantling of a network hosting several dark market URLs involved in trafficking stolen data and counterfeit goods. Law enforcement agencies collaborated internationally to execute coordinated operations, resulting in the seizure of multiple dark market sites and the arrest of key figures. These case studies highlight the effectiveness of strategic, well-planned operations that leverage technical expertise and intelligence sharing to target illegal online marketplaces. Seizing these URLs disrupts the operational capabilities of criminal organizations and reduces the availability of illicit products online.
Overall, law enforcement engagement targeting dark market URLs is a critical component of global efforts to combat cybercrime and illegal online activities. Through persistent investigation and strategic interventions, authorities can effectively reduce the presence of illicit marketplaces on the dark web, safeguarding users and maintaining lawful internet use. The ongoing fight against dark markets underscores the importance of technological innovation and international cooperation in addressing evolving cyber threats.
Implications of Dark Market URLs on Cybersecurity
The emergence of dark market URLs has significant implications for cybersecurity, as these hidden online platforms facilitate illicit activities beyond the reach of traditional law enforcement. These websites, often hosted on the Bitcoin network, obscure user identities and transactions, posing challenges for security professionals in tracking cybercriminal operations. The presence of dark market URL such as http://abacusborncrffug2ytuqx3fczqbou4mrev56pfliv7ipjfi4uib7cad.onion exemplifies the complexities involved in monitoring and combatting illegal online marketplaces. Understanding the infrastructure and operational mechanics of these dark market URLs is crucial for developing effective cybersecurity strategies to prevent exploitation and safeguard digital ecosystems.
Risks Associated with Dark Market URLs
Dark market URLs serve as gateways to clandestine online platforms where illicit goods and services are exchanged. These URLs are often hidden behind anonymizing technologies, making them difficult to trace and monitor. While they facilitate illegal transactions, they also pose significant cybersecurity threats that impact individual users, organizations, and national security. Understanding the implications of dark market URLs is essential for developing effective strategies to combat cybercrime and protect digital infrastructure.
One of the primary risks associated with dark market URLs is the proliferation of cybercriminal activities, including hacking, ransomware attacks, and distribution of malicious software. Cybercriminals frequently leverage these hidden online spaces to sell stolen data, hacking tools, and exploit kits. Visiting or interacting with these dark market sites—even unknowingly—can lead to malware infections, identity theft, and financial loss, directly compromising personal and organizational cybersecurity postures.
Furthermore, dark market URLs foster an environment where illegal transactions such as the sale of counterfeit products, illegal drugs, and weaponry occur. This underground economy often funds more sophisticated cyber threats, such as botnets and large-scale data breaches. The anonymity provided by these URLs makes it challenging for law enforcement agencies to track and dismantle these illicit networks, prolonging the threat landscape and increasing the potential for widespread cyber incidents.
Another critical implication is the increased risk of becoming a target for cyber espionage. Attackers may use dark market URLs to distribute spear-phishing campaigns, embed malicious links, or facilitate the exchange of sensitive espionage-related data. Organizations that inadvertently access or associate with these URLs risk exposing their networks to malicious actors, which can lead to intellectual property theft, strategic compromise, or operational disruption.
In conclusion, dark market URLs are a significant concern in the realm of cybersecurity. They serve as platforms that enable a range of illegal activities that threaten digital safety and stability. Vigilance, robust cybersecurity measures, and continuous monitoring are essential to mitigate the risks associated with these hidden online avenues, ultimately protecting individuals and organizations from potential harm.
Preventative Measures and Best Practices
Dark market URLs pose significant challenges to cybersecurity by serving as gateways to illicit activities, including illegal trade of stolen data, counterfeit goods, and malware distribution. These URLs often operate on hidden networks, making them difficult to track and shut down, thereby increasing the threat landscape for organizations and individuals alike. The presence of dark market URLs within cyberspace complicates efforts to detect malicious actors and hampers law enforcement in their investigations.
To mitigate the risks presented by dark market URLs, implementing robust preventative measures is crucial. This includes deploying advanced threat detection systems capable of identifying and blocking access to known malicious URLs. Regularly updating cybersecurity protocols and conducting comprehensive security awareness training for staff can reduce the likelihood of falling victim to phishing attacks or malware infections originating from dark markets. Furthermore, monitoring network traffic for abnormal patterns and leveraging threat intelligence feeds can help detect the presence of suspicious URLs such as dark market URLs.
- A select few of the dark-net vendor accounts identified were sourced to White House Market, according to court documents.
- The VS Code Marketplace has thousands of extensions supporting hundreds of programming languages and tasks.
- Despite law enforcement crackdowns, darknet markets continue to adapt and thrive.
- Christin says this moral stance underscores a truism for how black markets exist amid the threat posed by law enforcement.
Adopting best practices in cybersecurity also involves cooperation with law enforcement agencies and participation in information sharing initiatives. Organizations should establish clear incident response plans to address potential breaches linked to dark market traffic. Ensuring strong endpoint security, including antivirus software and multi-factor authentication, can prevent unauthorized access that might be facilitated through these illicit networks. By maintaining vigilance and adhering to a proactive security strategy, organizations can better shield themselves from the dangers associated with dark market URLs and reduce their overall cyber risk.
Emerging Trends in Dark Market URL Operations
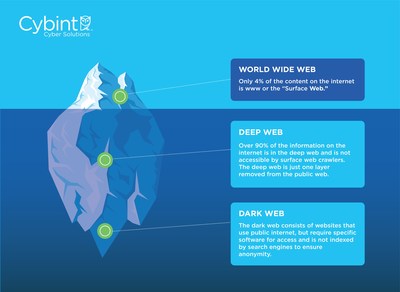
The landscape of dark market URL operations is continually evolving, reflecting new trends and emerging challenges in digital anonymity and security. As technological advancements and law enforcement tactics become more sophisticated, dark markets adapt by employing innovative strategies to maintain their presence and protect user privacy. Understanding these emerging trends is essential for researchers, cybersecurity professionals, and law enforcement agencies aiming to benchmark current practices and anticipate future shifts in dark market activities. For instance, the use of complex, encrypted URLs and decentralized hosting solutions exemplifies how these markets are shifting to more resilient infrastructures. Exploring these developments provides critical insights into the mechanisms that sustain these clandestine operations and highlights the importance of staying informed about changes in dark market URL operations, such as the increasing deployment of evolving access points like dark market URL.
Evolution of URL Domains and Hosting Strategies
Emerging trends in dark market URL operations reveal a dynamic landscape characterized by increased sophistication in domain management and hosting strategies. As dark markets evolve, operators continuously adapt their methods to enhance security, evade detection, and ensure operational continuity. One notable trend is the migration toward using more resilient and resilient domain structures, which often involve switching to alternative URL domains that are harder to identify or shut down. The shift helps maintain access to dark market platforms despite efforts to dismantle these operations.
Another significant development is the adoption of decentralized hosting strategies. Dark market operators increasingly leverage multiple hosting providers across different jurisdictions, making takedown attempts more complex. This diversification reduces dependency on any single hosting service and minimizes the risk of total shutdown. Additionally, many dark markets utilize fast-flux techniques, where the IP addresses behind a URL are continually changing, further complicating tracking efforts. These tactics also include frequently changing URLs within the dark market URL, making it harder for authorities to disrupt customer access.
Furthermore, the evolution of URL domains in the dark market space is influenced by efforts to evade detection through domain obfuscation strategies. Operators often register fresh domains, utilizing privacy protection services to conceal registration details. These new domains are then integrated into the dark market URL ecosystem to replace seized or decommissioned ones. This rapid turnover of URL domains underscores the importance of monitoring and updating threat intelligence to stay ahead of these malicious configurations.
Overall, the continual innovation in URL operations within dark markets demonstrates a resilient and adaptive ecosystem. Keeping pace with these trends requires proactive monitoring of domain registration patterns, hosting arrangements, and traffic analysis to identify and mitigate potential threats associated with these evolving dark market URLs.
Use of Decentralized and Resilient URL Systems
Emerging trends in dark market URL operations are significantly shaping the landscape of clandestine online activities. As the digital world evolves, operators of dark markets are increasingly adopting decentralized and resilient URL systems to enhance security, anonymity, and accessibility. These innovations facilitate more robust and adaptable infrastructure, making it challenging for authorities to disrupt illicit operations effectively. The use of advanced routing techniques and decentralized hosting solutions ensures that dark market URLs can withstand targeted takedowns and censorship efforts. This shift is evident in the way dark market platforms, such as dark market URLs, are now migrating toward decentralized architectures that distribute operational nodes across multiple jurisdictions, reducing the risk of shutdowns. Moreover, resilient URL systems incorporate redundancy and dynamic routing to maintain service availability even when parts of the network are compromised. These emerging approaches emphasize cryptographic security and anonymity features, which are critical for both users and operators seeking to evade detection. As these trends continue to develop, the dark market ecosystem is becoming increasingly sophisticated, leveraging resilient and decentralized URL operations to sustain its resilience against cybersecurity measures and law enforcement interventions. Ultimately, understanding these advancements is vital for developing effective countermeasures and policy responses aimed at mitigating illegal online activities originating from dark market platforms.


